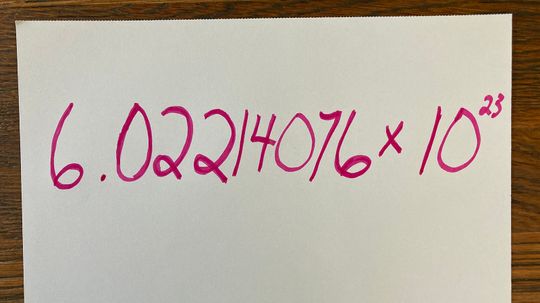Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter and the changes it undergoes during chemical reactions. In this section, learn about everyday chemistry, from chlorine beach to helium, and even why chocolate turns gray.

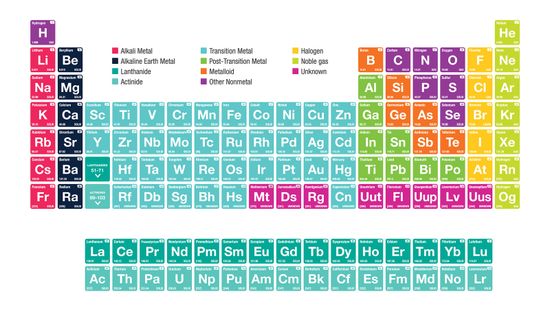
It's Elementary: The Periodic Table Quiz
Alkali Metals: Elements in the First Column of the Periodic Table

Cadmium: The Highly Toxic Metal That Powers the World
Strong Bases: Properties, Applications and Examples

Comparing Strong Acids and Weak Acids

10 Things You Should Never Mix With Alcohol

Delta-8 vs. Delta-9: Comparing Types of THC

What Color Is the Hottest Flame?

Why Do Bubbles Pop?
Learn More
"Delta 8" has become a bit of a buzzword in the cannabis industry and the community health sphere. But what exactly is delta-8, and how is it different from "regular" cannabis?
By Sascha Bos
In chemistry, the classification of substances into acids and bases is fundamental.
By Marie Look
In the world of chemistry, understanding the difference between strong acids and weak acids is fundamental for both students and professionals alike. Strong acids are known for their ability to completely dissociate in water, making them a pivotal topic in chemical reactions and laboratory experiments.
Advertisement
Flame colors span a spectrum that tells a tale as old as fire itself. Many people wonder what color is the hottest flame; more than a testament to the natural fascination with fire's beauty, this question underscores a fundamental principle in the science of thermodynamics and combustion.
All bubbles pop — that's a fact of life. But what's the science behind the short life and inevitable pop of a bubble?
It’s the ultimate cheat sheet for science class — and it’s right there hanging on the wall. What do you really know about the indispensable periodic table of elements?
Juice and soda mix well with alcohol, but a few things don't mix so well. Some may just produce embarrassing moments. Others could cost you your life.
By Beth Brindle
Advertisement
Why do newspapers turn yellow over time?
I have heard that carbon monoxide is extremely poisonous. Can you explain why?
Scenario: A helium balloon is up against the ceiling one day, and the next day it's on the floor. Does the balloon fall because the helium leaks out, or because the helium molecules slow down due to decreased pressure?
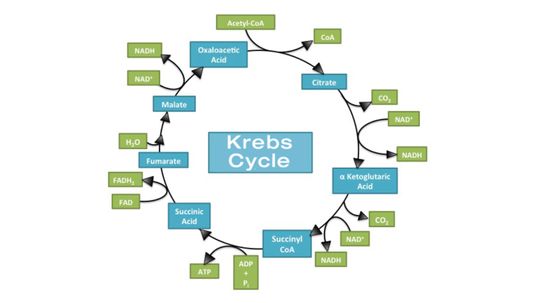
The main function of the Krebs cycle is to produce energy, stored and transported as ATP or GTP, to keep the human body up and running.
Advertisement
Superacids are those with an acidity greater than sulfuric acid. So which is the most super of superacids and what exactly is it used for?
Discovered in the early 1800s from a chunk of smuggled platinum ore, rhodium is the most valuable precious metal on the planet today, used mainly for keeping car emissions in check.
Cadmium is a natural metal and the leading component in rechargeable batteries and solar cells. It is also highly toxic and heavily regulated.
First there was Volvo. Then came IKEA. Well get ready for the next major Swedish export: snus, a smokeless tobacco product, similar to dip or chew.
Advertisement
That's one seriously big number, and technically Amedeo Avogadro didn't even come up with it. So how did the Italian chemist make such an indelible (numerical) mark on the wonderful world of chemistry?
These small molecules are the foundation for much bigger things, from ordinary household products around us to essential components within our bodies.
Polymers are the basic components in so many of the products we use each day.
At the same time scientists discovered that nitrous oxide could numb agonizing pain, they also found it could make you really lightheaded and silly. Yes, huffing parties started in the 1700s.
By Dave Roos
Advertisement
If you've ever had a half-frozen beer explode on you, you know that yes, alcohol freezes — but not all types freeze at the same rate. We'll let you in on the secrets to frozen alcoholic delights.
Denatured alcohol is useful for lots of things, but drinking definitely isn't one of them.
Diatomic elements are molecules composed of only two atoms, every time, always. There are only seven of them on the entire periodic table.
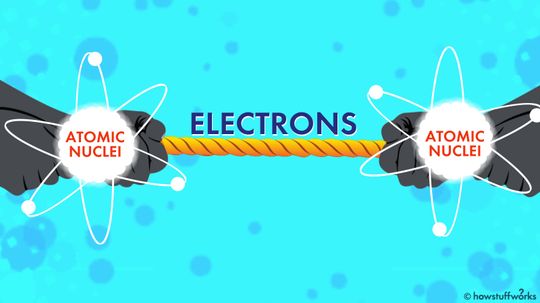
Electrons are attracted to some atoms more than others. If two atoms are of equal strength, the electrons will be equally shared. If one atom is stronger, the electrons will be pulled in that atom's direction.
Advertisement
The two different types of alcohol are commonly used in hand sanitizer today. But does one work better than the other?
Don't know your fool's gold from the real deal? We'll tell you how to tell what's pyrite (aka fool's gold) and the good ol' 24 karat stuff you want.
By Mark Mancini