Geology
Geology is the study of the composition and physical properties of rocks, minerals, gems and other related earth materials, including diamonds and crystals. Scientists gain an understanding of the Earth's history by studying its composition.

Is Africa Splitting in Two? Really? Here's the Scoop

What Exactly Is the Eye of the Sahara, aka the Richat Structure?

The Driest Place on Earth: Chile's Atacama Desert

7 Power Crystals for Protection and Positive Energy

Carnelian Meaning: Healing Properties, Benefits, & Symbolism

Creating Crystal Grids: A Step-by-Step Guide

Velociraptor Alert: The Feathered Dinosaur Quiz

The Rockin' State Fossils Quiz

10 Extinct Hominids
Learn More / Page 3
Carbon-14 dating is something that you hear about in the news all the time. Everything from mastodons to the Shroud of Turin has been dated using this technique! Learn about how carbon-14 dating works and why it is so accurate!
Everyone knows that once a bone has fossilized, it's hard as a rock, right? So how did scientists find soft tissue inside a broken dinosaur bone?
Diamonds are beautiful and popular - but not everyone can afford these gems. While man-made versions are less expensive, most lack the luster and brilliance of the real thing, except moissanite. See how it compares!
By Melissa Russell-Ausley
Advertisement
You likely heard that paleontologists uncovered a cache of dinosaur embryos, bone fragments and eggshells in China. You also may recall that we've made crazy leaps forward in genetics and genomics. Can we put the two together and create a dinosaur?
The sea scorpion may have been the largest bug to ever live on the Earth, according to a recent find. Learn more about the giant sea scorpion.
By Josh Clark
Are dinosaurs real? Most people don't have to travel too far to answer that question in the affirmative with some kind of exhibit displaying dinosaur fossils. Or simply look at any bird you can see outside your home.
The 1993 movie "Jurassic Park" did a good job of bringing the idea of cloning dinosaurs into popular culture. It portrayed dinosaur cloning in a way that made sense to a lot of people, but is it really possible?
Advertisement
Every time a new fossil is found, one of the first things scientists determine is how old that fossil really is. But how do they determine it, and how can they be completely accurate?
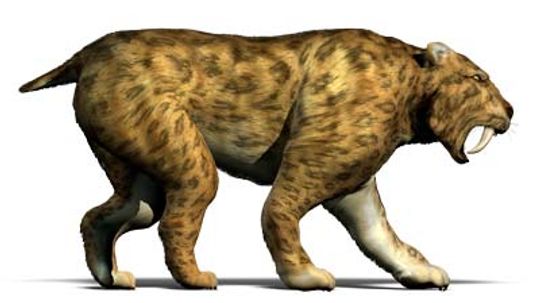
Saber-tooth cats have long been likened to tigers, but they aren't tigers at all. While they share some physical traits and hunting practices with tigers, saber-tooth cats are also quite different.
Earthquakes and volcanoes get all the press. But the landslides they trigger are often more devastating. What makes the ground suddenly rip downhill, taking trees and homes with it?
Fossils tell a story, much like the clues at the scene of a crime. Researchers look for evidence and paleontologists study that evidence to answer questions about the past.
Advertisement
From the Hope diamond to the shiny bits in instant coffee, crystals have always held the power to fascinate us humans. Are they more than just a bunch of pretty facets?
One term might give you the impression of something grand and mysterious, while the other makes you think of claustrophobia-inducing environs that threaten human life. But what's the real difference?
Researchers discovered that everyone's favorite prehistoric cat had some seriously big bones — even as a youngster.
By Robert Lamb
Not all fossils are found on dry land. In fact some of the most fascinating fossil finds in history have been submerged for centuries.
By Mark Mancini
Advertisement
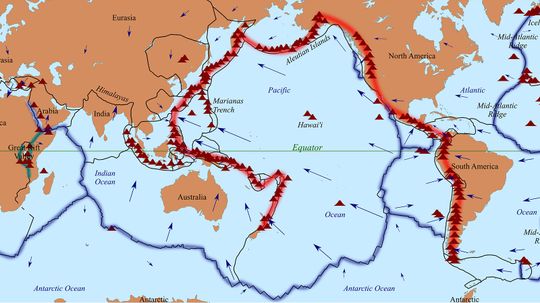
The Pacific's Ring of Fire is a 25,000 mile long "ring" that's home to 75 percent of all the world's volcanic activity and 90 percent of the planet's earthquakes. So what makes this area so active?
By Mark Mancini
The U.S. is full of exceptional geological formations. But these five set the bar high as far as landmarks go.
By Mark Mancini
This white-hot metal not only makes beautiful jewelry, it's coveted for industrial, medical and military purposes too.
By Alia Hoyt & Desiree Bowie
Permafrost across the globe is rapidly melting. What could this mean for the future of the planet?
By Mark Mancini
Advertisement
Let's take a look at some of the strongest metals on Earth and their surprising uses.
By Dave Roos & Sascha Bos
Cobalt is associated with the color blue, but it's so needed for rechargeable batteries that the U.S. put it on the list of minerals it can't live without.
By Dave Roos
Cultures all over the world have treasured turquoise for its color and rarity for thousands of years — from Native American jewelry and Aztec and Mesoamerican art to King Tutankhamun's death mask.
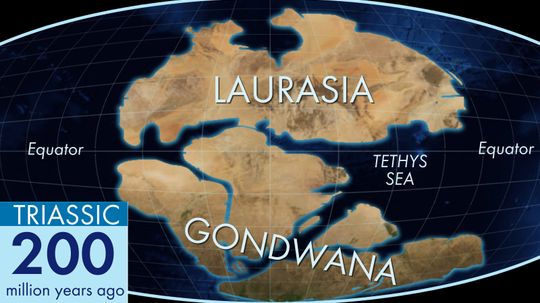
Discover the origins of the continental drift theory and how scientists explain these geologic phenomena.
Advertisement
Gondwana was a humongous landmass that persisted for 300 million years before it began to break up, forming all the continents in the modern Southern Hemisphere.
Mountain Lake in Virginia is best known for its starring role in 'Dirty Dancing.' But today, it's nothing more than a muddy pit that's all but dried up ... and geologists think they may know why.