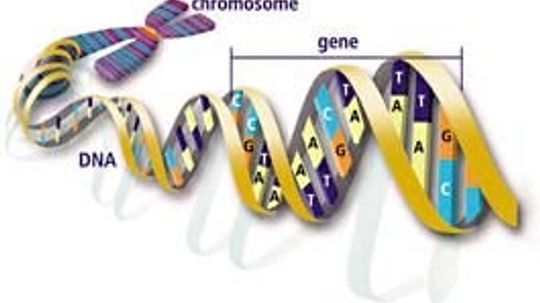
Genetic Science
Genetics is the study of cellular science. It furthers our understanding of how DNA and the genetic make-up of species and can lead to cures for diseases and shape our future.

Why do people sing in the shower?

10 Bizarre Treatments Doctors Used to Think Were Legit

Ancient Egyptian Pregnancy Test Survived Millennia Because It Worked

Can You Crack This Nuts Quiz?

The Science Behind Your Cat's Catnip Craze

Corpse Flower: When Nature Deceives

Hypertonic vs. Hypotonic Solutions: Differences and Uses

Your Phone Is a Germ Factory, So Stop Taking It to the Toilet

Why Even Identical Twins Have Different Fingerprints

Howstuffworks Interviews: Extinction Level Events with Annalee Newitz

What will the Earth look like in 50,000 years?

How did language evolve?

Differences Between Pet Training and Animal Conditioning

What Is Shadow Work and How Does It, Well, Work?

Why can't we remember being babies?
Learn More
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the average height in the United States is 5 feet, 9 inches (1.75 meters) for adult men and 5 feet, 3.5 inches (1.61 meters) for adult women. But some people can reach heights upwards of 7 or 8 feet (2.1 to 2.4 meters)!
By Sascha Bos
Before the widespread use of DNA, establishing the paternity of a child was a tricky business. Ever heard of the oscillophore?
By Dave Roos
After scientists announced the first draft of the human genome, people began to wonder how our new understanding of DNA would change life. Several research institutes stated the accomplishment would revolutionize science and modern medicine -- but how, exactly?
Advertisement
What's more fun than looking at pictures of DNA and celebrities? Check out Dolly, dimples and dominant and recessive traits in this fun gallery charting how genetics play out in humans (and a few animals).
How can children from the same parents look so different? I mean, why don't all kids from the same parents look exactly alike, since the parents just have one set of chromosomes each and they don't change?
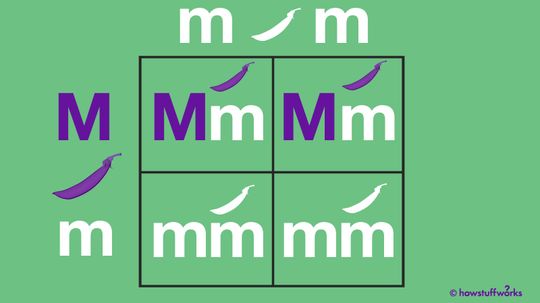
A Punnett square helps predict the possible ways an organism will express certain genetic traits, such as purple flowers or blue eyes.
CRISPR is the genius behind innovations that seemed impossible a decade ago. Could you grow tomatoes with the kick of hot sauce or ferment wine that doesn't cause a hangover? That's just two of the things scientists are looking into.
Advertisement
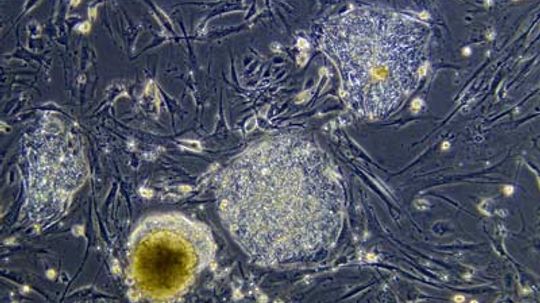
This week, a group of London-based scientists requested official permission to begin a three-year study involving stem cells derived from human-cow hybrids.
By Julia Layton
Hereditary illnesses are passed down from parents to their children like gene traits, and children might inherit a disease even though their parents never suffered from its symptoms. Learn about hereditary illnesses.
By Alvin Eden & Elizabeth Eden
It sounds kind of great, right? Imagine everything you and yourself could get done. You'd be masters of the world -- wouldn't you?
By Robert Lamb
Ever hear that urban legend about waking up without your kidney? Would organ thieves have to find a new line of work if cloned organs became a reality?
Advertisement
Who hasn't fantasized about bigger biceps? Killer abs? A rear end you could bounce a quarter off? But would you tamper with your genes to achieve that buff body?
How would you like to be the person responsible for changing science and Western civilization? With the "Origin of Species," Charles Darwin did. How did this English gent become the reluctant ambassador of evolution?
By Robert Lamb
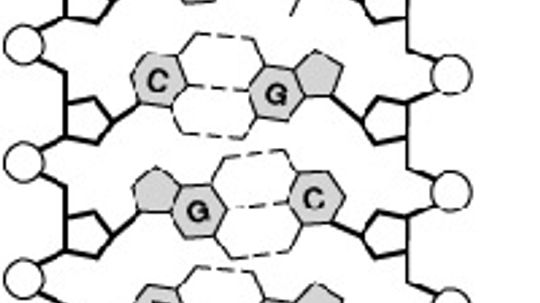
More than 50 years have passed since Watson and Crick untangled the structure of DNA and five years have elapsed since scientists finished sequencing the entire human genome. What have we figured out about our genetic material?
That bowling ball of white meat in your oven is a far cry from its wild ancestors. How did a single breed of top-heavy, dim-witted birds come to dominate the turkey market?
Advertisement
Many old couples tend to look like each other due to shared life experiences, according to a recent study. Learn more about why older couples look alike.
Hair loss affects millions of Americans -- men, women and even children. That's why a recent gene therapy study from a research group at the University of Pennsylvania has many people excited.
Much like Noah, researchers are stockpiling the genes of Earth's living creatures, loading them into state-of-the art facilities and freezing them. Are scientists saving them for a rainy day?
By Robert Lamb
Can humans live forever? No, but thanks to the discovery of the Hayflick limit, we know that cells can conceivably divide forever without dying.
By Josh Clark
Advertisement
Doctors always want your blood, but one day, a health care professional may ask you to open up and say, "Ptooey!" Why? Your spit holds a mother lode of biological information.
Given the choice, would you rather have been born with a different eye color, hair color or skin tone? Of course, you didn't have these options, but could you have them for your own children?
By Kevin Bonsor & Julia Layton
The CBS drama "CSI: Crime Scene Investigation" routinely uses cutting-edge technology to solve crimes, including collecting and analyzing DNA evidence. But catching a criminal using DNA evidence is not quite as easy as "CSI" makes it seem.
Cloning is the process of making a genetically identical organism through nonsexual means. In this article, we will examine how cloning works and look at possible uses of this technology.
Advertisement
What is the difference between a hardwood and a softwood? How hard does a tree have to be to be considered hardwood?
With movie titles like "Attack of the Clones" and "The Clone Wars," it's no wonder human cloning makes us anxious. As scientists make startling discoveries cloning animals, are humans next?
By Kevin Bonsor & Cristen Conger