Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter and the changes it undergoes during chemical reactions. In this section, learn about everyday chemistry, from chlorine beach to helium, and even why chocolate turns gray.

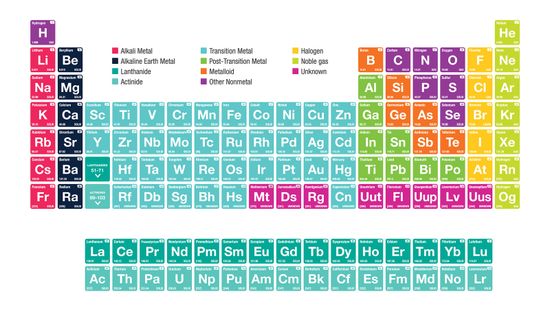
It's Elementary: The Periodic Table Quiz
Alkali Metals: Elements in the First Column of the Periodic Table

Cadmium: The Highly Toxic Metal That Powers the World
Strong Bases: Properties, Applications and Examples

Comparing Strong Acids and Weak Acids

10 Things You Should Never Mix With Alcohol

Delta-8 vs. Delta-9: Comparing Types of THC

What Color Is the Hottest Flame?

Why Do Bubbles Pop?
Learn More
"Delta 8" has become a bit of a buzzword in the cannabis industry and the community health sphere. But what exactly is delta-8, and how is it different from "regular" cannabis?
By Sascha Bos
In chemistry, the classification of substances into acids and bases is fundamental.
By Marie Look
In the world of chemistry, understanding the difference between strong acids and weak acids is fundamental for both students and professionals alike. Strong acids are known for their ability to completely dissociate in water, making them a pivotal topic in chemical reactions and laboratory experiments.
Advertisement
Flame colors span a spectrum that tells a tale as old as fire itself. Many people wonder what color is the hottest flame; more than a testament to the natural fascination with fire's beauty, this question underscores a fundamental principle in the science of thermodynamics and combustion.
All bubbles pop — that's a fact of life. But what's the science behind the short life and inevitable pop of a bubble?
It’s the ultimate cheat sheet for science class — and it’s right there hanging on the wall. What do you really know about the indispensable periodic table of elements?
Juice and soda mix well with alcohol, but a few things don't mix so well. Some may just produce embarrassing moments. Others could cost you your life.
By Beth Brindle
Advertisement
Why do newspapers turn yellow over time?
I have heard that carbon monoxide is extremely poisonous. Can you explain why?
Scenario: A helium balloon is up against the ceiling one day, and the next day it's on the floor. Does the balloon fall because the helium leaks out, or because the helium molecules slow down due to decreased pressure?
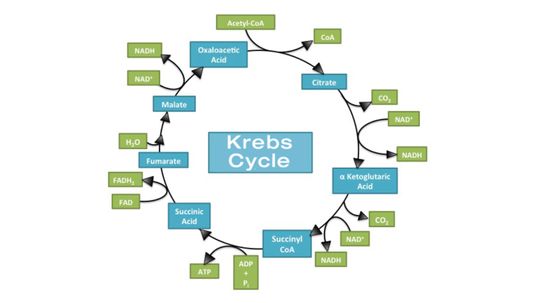
The main function of the Krebs cycle is to produce energy, stored and transported as ATP or GTP, to keep the human body up and running.
Advertisement
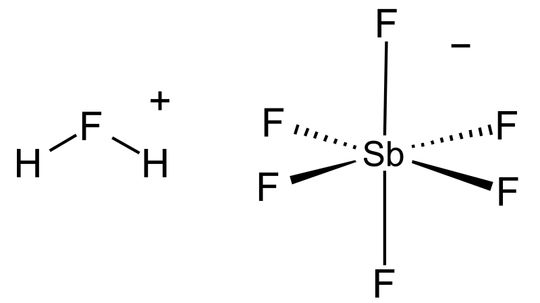
Superacids are those with an acidity greater than sulfuric acid. So which is the most super of superacids and what exactly is it used for?
Discovered in the early 1800s from a chunk of smuggled platinum ore, rhodium is the most valuable precious metal on the planet today, used mainly for keeping car emissions in check.
Cadmium is a natural metal and the leading component in rechargeable batteries and solar cells. It is also highly toxic and heavily regulated.
Have you seen investigators on crime shows who spray some stuff on a "clean" carpet and suddenly -- blood stains! Well, of all the fictional technology on TV, it turns out this stuff is real! Find out how luminol reveals the blood.
By Tom Harris
Advertisement
If water is made up of hydrogen and oxygen, why can't we breathe underwater? It has to do with how molecules combine and how the human lung functions.
Ever wondered exactly what they "artificial flavors" in your candy are, and why no specific ingredients are listed? Find out in this article.
If you were to touch dry ice, it wouldn't be anything like touching water ice. So what's it like? Is it hot or cold? And would it leave a mark?
We've all been told not to put aluminum foil in the microwave. Stories of incredible explosions and fires are usually at the center of these ominous warnings. Why is that?
Advertisement
Imagine spending your days racked with pain or losing pound upon pound because nausea leaves you unable to eat. Now imagine that someone offers you a wonder drug to cure all your ills. The problem? It's illegal.
Once considered a semiprecious metal alongside gold and silver, aluminum pretty much languished in obscurity until the 19th century. How did the metal become so ubiquitous?
Can you pass the acid test? That electric Kool-Aid changed the fabric of 1960's American counterculture. So, what's it's like to trip on LSD?
It begins with an unassuming "H" and ends in crazy elements that you've likely never heard of. But the periodic table, encapsulated on a mere sheet of paper, can be a scientist's best friend and a testament to our human drive to organize the world.
Advertisement
When it comes to stimulating the human central nervous system, meth can hold its shaky, toothless head high. Why is this drug so additive?
We love it. We wear it glittering around our necks and sparkling at our ears, wrists and feet. We pass it down to our children and hoard it in secret stashes. Why is this precious metal so prized?