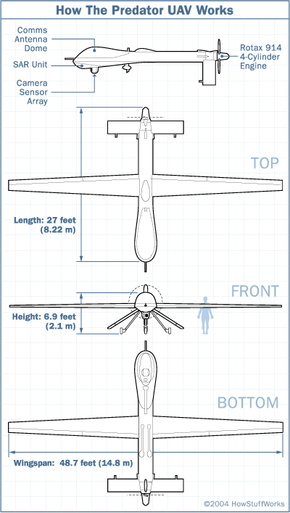
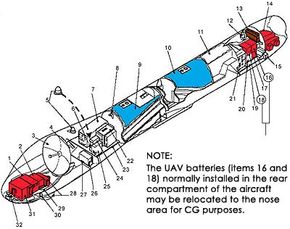
In 2018, the U.S. military made the strategic decision to retire the aging MQ-1 Predator drones due to technological advancements and evolving mission requirements. This transition was marked by the introduction of the MQ-9 Reaper, signifying a significant leap in UAV performance.
The MQ-9 Reaper made its debut in the early 2000s, representing a remarkable improvement over its predecessor. It boasts a higher maximum altitude, extended endurance and a larger payload capacity, equipping it to carry a broader array of sensors and munitions for a wide range of mission profiles.
Most notably, the Reaper features enhanced firepower, capable of deploying a variety of munitions, including Hellfire missiles and precision-guided bombs, making it a versatile platform for both intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance (ISR) and combat missions.
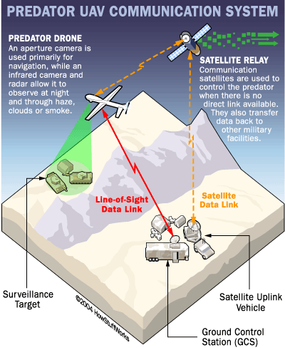
With its extended operational range, the Reaper can cover vast areas and maintain station for prolonged periods, a pivotal capability for ISR and strike missions. The inclusion of advanced communication systems further enhanced connectivity with ground stations and other assets. Moreover, select Reaper variants are designed with stealth features, enhancing their survivability in hostile environments.
Several Reaper variants were developed to cater to specific mission requirements. Among these are the MQ-9A Reaper, the initial armed version, and the MQ-9B Reaper, featuring enhanced endurance and autonomous capabilities. Additionally, the MQ-9 SeaGuardian variant was adapted for maritime surveillance and patrol tasks, including coastal and maritime border monitoring.
The retirement and replacement of the MQ-1 Predators was driven by the imperative to adapt to emerging threats and evolving demands of modern warfare. While the MQ-1 Predators played a crucial role in the early era of UAV technology, the MQ-9 Reaper's substantial technological advancements in performance and firepower rendered it a more versatile and capable platform for contemporary military operations.
With the proliferation of remotely operated and automated combat units, the trend in military technology seems to be moving toward missions carried out by automated warriors, with the flesh-and-blood controllers battling safely from behind computer terminals.
This article was updated in conjunction with AI technology, then fact-checked and edited by a HowStuffWorks editor.