Gears are used in tons of mechanical devices. Most importantly, they provide a gear reduction in motorized equipment. This is key because often a small motor spinning very fast can provide enough power for a device, but not enough torque, the force that causes an object to rotate on an axis or twist. For instance, an electric screwdriver has a very large gear reduction (reduction in the speed of a rotary machine such as an electric motor) because it needs lots of torque to turn screws. But the motor only produces a small amount of torque at a high speed. With a gear reduction, the output speed can be reduced while the torque is increased.
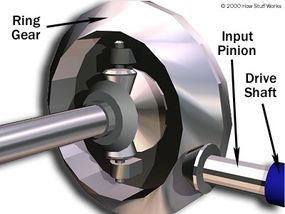
Gears also change the direction of rotation. For instance, in the differential between the rear wheels of your car, the power is transmitted by a shaft that runs down the center of the car, and the differential has to turn that power 90 degrees to apply it to the wheels.
Advertisement
There are a lot of intricacies in the different types of gears. In this article, we'll learn exactly how the teeth on gears work, and we'll talk about the different types of gears you find in all sorts of mechanical gadgets.