Crack in the Body
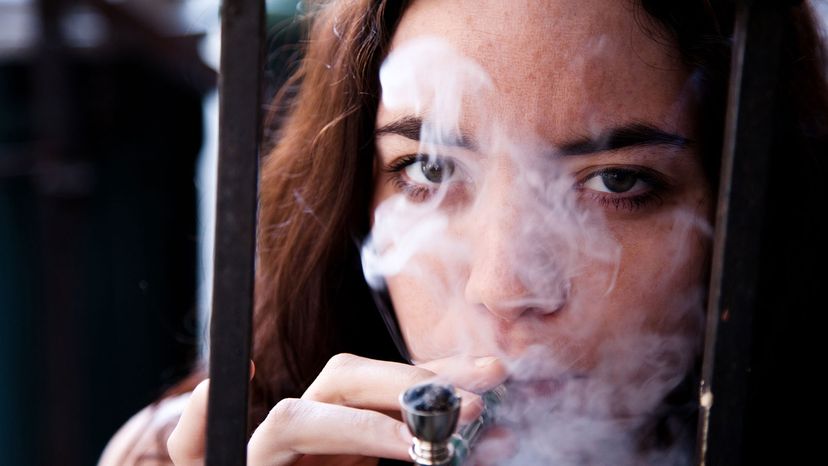

Most users smoke crack, although in rare cases, they may inject it [source: Drug Policy Alliance]. To smoke crack cocaine, the user places the drug into a small glass pipe (sometimes called a "straight shooter"). He or she then places a small piece of a steel wool at one end of the pipe tube and puts the rock on the other side of this filter. When the rock is heated from below, it produces a vapor, or smoke. The user inhales that vapor into his or her lungs. From there, the drug is taken up by the person's bloodstream.
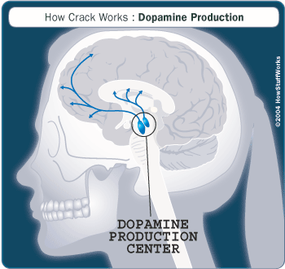
When it gets into the body, crack acts upon a midbrain structure called the ventral tegmental area (VTA), where a chemical messenger in the brain called dopamine lives [source: National Institutes of Health]. Crack interferes with dopamine, which is involved in the body's pleasure response. Dopamine is released by cells of the nervous system during pleasurable activities such as eating or having sex. Once released, dopamine travels across a gap between nerve cells, called a synapse, and binds to a receptor on a neighboring nerve cell (also called a neuron). This sends a signal to that nerve cell. (Dopamine doesn't actually cause feelings of pleasure but it does influence how pleasure affects the brain, usually by reinforcing a pleasant feeling.) Under normal conditions, once the dopamine sends that signal, it is reabsorbed by the neuron that released it. This reabsorption happens with the help of a protein called the dopamine transporter [source: National Institutes of Health].
Advertisement
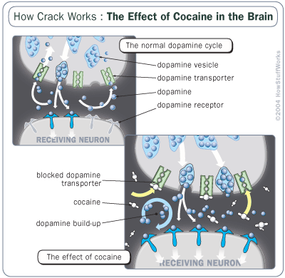
Crack interrupts this cycle. It attaches to the dopamine transporter, preventing the normal reabsorption process. As dopamine builds up in the synapse, it continues to stimulate the receptor, creating a lingering feeling of exhilaration or euphoria in the user.
Because crack is inhaled as a smoke, it reaches the brain much faster than inhaled powder cocaine. It can get to the brain and create a high within three to five minutes, compared to the 20 to 30 minutes it takes to feel the effects of snorted cocaine. On the downside, the crack cocaine high lasts about 30-60 minutes, while the cocaine high could last one to two hours [source: American Addiction Centers].