Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter and the changes it undergoes during chemical reactions. In this section, learn about everyday chemistry, from chlorine beach to helium, and even why chocolate turns gray.

The Most Expensive Metal in the World Isn't Gold or Platinum

It's Elementary: The Periodic Table Quiz
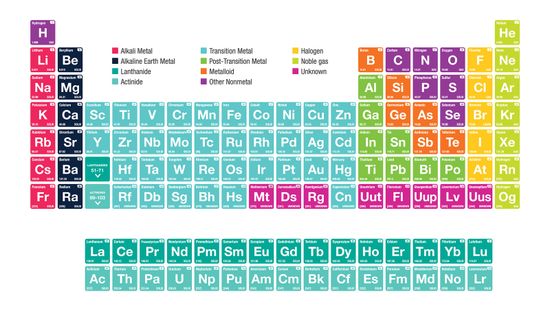
Alkali Metals: Elements in the First Column of the Periodic Table

7 Types of Alcohol for Drinking, Cleaning and More

Understanding the Empirical Formula in Chemistry
Strong Bases: Properties, Applications and Examples

Delta-8 vs. Delta-9: Comparing Types of THC

What Color Is the Hottest Flame?

Why Do Bubbles Pop?
Learn More
From cocktails to cooking, alcohol is everywhere. But not all alcohol is created equal. The types of alcohol range from drinkable spirits to industrial solvents, each with different uses, chemical properties and risks.
In chemistry, there are a variety of methods that scientists use to identify a chemical compound, including a molecular formula, molar mass and molecular diagram. The simplest formula of these is known as the empirical formula.
By Talon Homer
Precious metals are not just shiny and attractive; these elements are also incredibly valuable, often used in a wide range of industries from jewelry to high-tech applications.
By Mack Hayden
Advertisement
"Delta 8" has become a bit of a buzzword in the cannabis industry and the community health sphere. But what exactly is delta-8, and how is it different from "regular" cannabis?
By Sascha Bos
In chemistry, the classification of substances into acids and bases is fundamental.
By Marie Look
In the world of chemistry, understanding the difference between strong acids and weak acids is fundamental for both students and professionals alike. Strong acids are known for their ability to completely dissociate in water, making them a pivotal topic in chemical reactions and laboratory experiments.
Flame colors span a spectrum that tells a tale as old as fire itself. Many people wonder what color is the hottest flame; more than a testament to the natural fascination with fire's beauty, this question underscores a fundamental principle in the science of thermodynamics and combustion.
Advertisement
All bubbles pop - that's a fact of life. But what's the science behind the short life and inevitable pop of a bubble?
It's the ultimate cheat sheet for science class - and it's right there hanging on the wall. What do you really know about the indispensable periodic table of elements?
Juice and soda mix well with alcohol, but a few things don't mix so well. Some may just produce embarrassing moments. Others could cost you your life.
By Beth Brindle
Why do newspapers turn yellow over time?
Advertisement
Scenario: A helium balloon is up against the ceiling one day, and the next day it's on the floor. Does the balloon fall because the helium leaks out, or because the helium molecules slow down due to decreased pressure?
I have heard that carbon monoxide is extremely poisonous. Can you explain why?
Marijuana isn't just a recreational drug for hippies and philosophy majors -- its psychoactive history ranges from Egyptian mummies to modern U.S. politics. What's the big deal about this leafy, green plant?
By Kevin Bonsor & Nicholas Gerbis
You know how chocolate sometimes turns white? Why does that happen and is it still OK to eat?
Advertisement
Have you seen investigators on crime shows who spray some stuff on a "clean" carpet and suddenly -- blood stains! Well, of all the fictional technology on TV, it turns out this stuff is real! Find out how luminol reveals the blood.
By Tom Harris
Here's something to consider: The place you call home likely has walls and glass windows. Both are adept at keeping rain, snow and wind from bothering you in your abode. Only one, though, allows light to enter. Why is that?
More than 2.3 billion people across the globe drink alcohol, but most don't consider it a drug. But if you've ever seen someone who's had too much, you know alcohol has profound effects on the mind and body.
Smoking or chewing tobacco makes many people feel good, even mildly euphoric. It's the nicotine that produces the buzz. Find out how nicotine affects the human body and what makes it so addictive.
Advertisement
Biting on aluminum foil can be painful -- basically, when you bite on foil, you build a battery in your mouth. Ouch!
The air we breathe contains 21 percent oxygen. Would we be better off breathing 100 percent oxygen?
Rust is the common name for iron oxide, which is created when iron bonds with oxygen. In fact, pure iron is only rarely found in nature because it interacts with oxygen so easily.
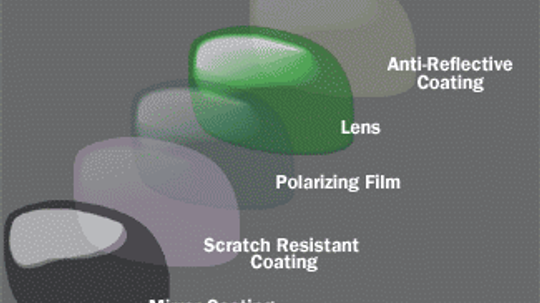
I recently bought a pair of mirrored sunglasses and they are already scratched. Isn't there a way to make them scratch-resistant?
Advertisement
If you were to touch dry ice, it wouldn't be anything like touching water ice. So what's it like? Is it hot or cold? And would it leave a mark?
We've all been told not to put aluminum foil in the microwave. Stories of incredible explosions and fires are usually at the center of these ominous warnings. Why is that?