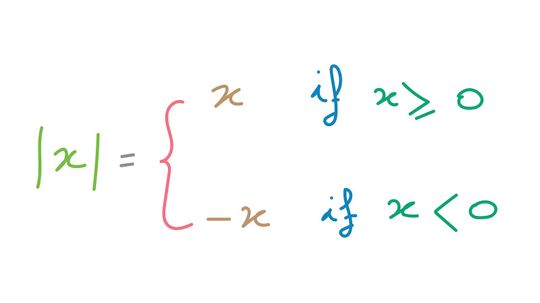Physical Science
Physical science is the study of the physical world around you. Learn about everything from electricity to magnetism in this section.
Brown Noise vs. White Noise: Which Is Best for Quality Sleep?

Can a sound wave kill you?

Can two cans and a string really be used to talk over a distance?

7 Types of Alcohol for Drinking, Cleaning and More

Understanding the Empirical Formula in Chemistry

The Most Expensive Metal in the World Isn't Gold or Platinum

How Electricity Works

How Faraday Cages Work

How Gasoline Works

What Does Mummification Have to Do With Gene Hackman?

What do bugs have to do with forensic science?

5 Things You Didn't Know About Autopsies

How Alchemy Paved the Way for Chemistry

How did Nikola Tesla change the way we use energy?

Time May Not Exist, Say Some Physicists and Philosophers

Why Does Ice Stick to Your Fingers?
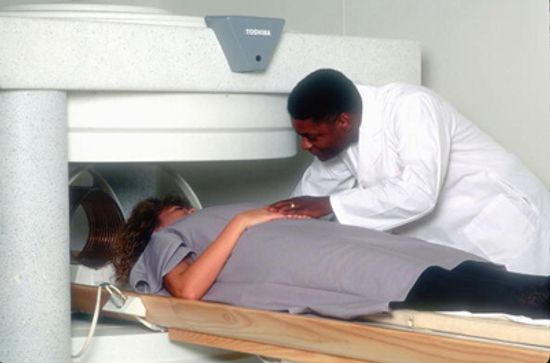
What if I forgot to remove a piercing before an MRI?
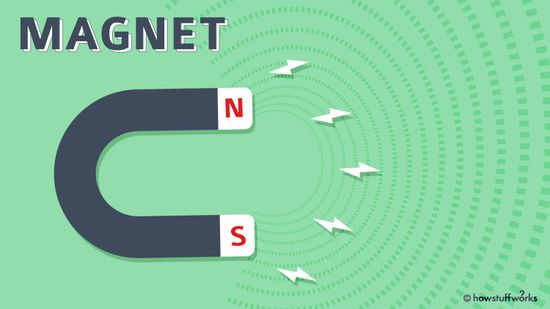
A Kid-friendly Introduction to Magnets and Magnetism
What's the Hardest Math Problem in the World? Try These 9

8 Types of Data That Inform Insights and Relationships

Congruent Angles: Definition, Symbol and Key Theorems

Tonnes vs. Tons: Metric vs. Imperial Measurements Strike Again

The Most Expensive Liquid Is 26,000x the Price of Human Blood

5 Hugely Fun Facts About Mass (Not Weight)

The Demon Core: A Tale of Atomic Ambition and Tragic Fate

Half-Life Formula: Components and Applications

Could an 'X17 Particle' Hint at a Fifth Force in the Universe?

Why Are School Buses Yellow?

HowStuffWorks: How To Draw An Impossible Shape
What Are the Colors in the Visible Spectrum?
Learn More
Mathematics is filled with complex challenges, but the hardest math problem in the world isn’t just a difficult question on a school test: It’s one that defies centuries of logic, calculation, and creativity.
If you’ve ever priced out cargo or read about a ship carrying coal, grain or bricks, you’ve seen tonnes vs. tons. These two words look similar yet refer to different systems and units. In international trade and technical writing, that small spelling shift changes real-world numbers.
Different problems require different kinds of information, and understanding the types of data is the first step to choosing the right analysis techniques.
Advertisement
From lifesaving medical components to everyday essentials, the most expensive liquid on Earth isn’t always what you'd expect. These liquids are priced by rarity, production difficulty, and real-world value — and some cost far more per liter than gold.
From cocktails to cooking, alcohol is everywhere. But not all alcohol is created equal. The types of alcohol range from drinkable spirits to industrial solvents, each with different uses, chemical properties and risks.
Ever wondered why some dead bodies last for thousands of years while others break down into dust? That's where the science of mummification comes in. Whether it's through ancient rituals, boggy swamps or some truly extreme self-imposed methods, mummified human remains give us an incredible look into history, biology and even chemistry.
"Why are there so many songs about rainbows?" sings Kermit the Frog in a song (about rainbows) called "Rainbow Connection" from 1979's "The Muppet Movie." And it's not just songs that feature rainbows. Children's memorabilia (from "My Little Pony" to Lisa Frank to anything with unicorns) and sweet treats ( from Lucky Charms to sherbert) are all filled with these dazzling rainbow colors.
By Ada Tseng
Advertisement
Ever wondered what the most abundant element on Earth is? Or how the elements that make up our planet compare to those floating out in the vast universe?
By Mack Hayden
Two congruent angles are simply pairs of angles with equal measures. You can find congruent angles examples in hundreds of everyday objects.
By Mitch Ryan
Adjacent angles are one of the earliest and most important concepts to learn in basic geometry, as they have applications in further subjects like trigonometry, physics, and engineering. Effective students of geometry should be able to identify adjacent angles on sight and calculate them to a great degree of accuracy without a protractor.
By Talon Homer
When pursuing an education in mathematics and algebra, one of the earliest and most important concepts to understand is the associative property, also known as the associative law.
By Talon Homer
Advertisement
In chemistry, there are a variety of methods that scientists use to identify a chemical compound, including a molecular formula, molar mass and molecular diagram. The simplest formula of these is known as the empirical formula.
By Talon Homer
In the subjects of geometry and trigonometry, a linear pair of angles is any two adjacent angles formed together to add up to 180°, or π (pi) radians.
By Talon Homer
Precious metals are not just shiny and attractive; these elements are also incredibly valuable, often used in a wide range of industries from jewelry to high-tech applications.
By Mack Hayden
With its three sides and three angles, the triangle is one of the most basic shapes in geometry. This means calculating the area of a triangle is a fundamental skill in geometry, with multiple formulas available depending on the type of triangle and the given data.
By Marie Look
Advertisement
In your study of math, you will likely come across the concept of factors at a certain point. While this can be daunting if you've never encountered it before, it won't take long before you're able to determine all the factors of a particular number.
By Zach Taras
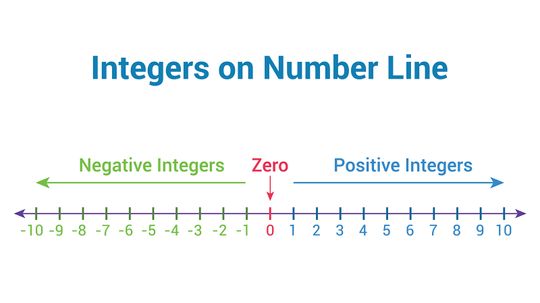
Integers are natural numbers (or whole numbers) that stem from the Latin word meaning "intact." In other words, any two integers will be rational numbers. A rational number is a value without fractional part or decimal remainders.
By Mitch Ryan
A rectangular prism is a three-dimensional cuboid figure. In the same way that a triangular prism brings three connected lines to life in the real world, a rectangular prism takes the length and width of two-dimensional rectangles to the next level by adding height into the equation.
By Mitch Ryan
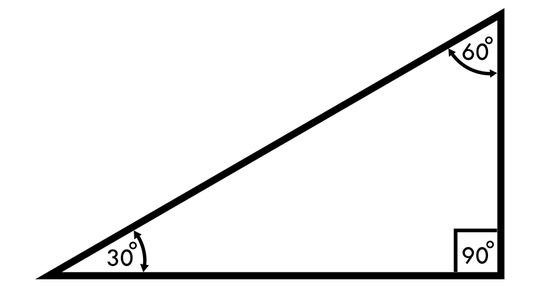
Anyone who's ever faced mind-numbing trigonometry problems and practice questions will be familiar with the Pythagorean Theorem and its square root principles in the 30-60-90 triangle. This special triangle has several short-cut rules to help new mathematicians find interior angles and linear lengths quickly.
By Mitch Ryan
Advertisement
In algebra and calculus, a polynomial function is used to chart out graphs and waves with much more complexity than a simple linear factor. Polynomial division is sometimes required to factor them, and cut them up into chunks that we humans can better understand.
By Talon Homer
Arcs are an important aspect of geometry, physics, trigonometry and design work. However, curved lines are much more difficult to measure than straight lines, which is why it's important to familiarize yourself with the arc length formula.
By Talon Homer
The interquartile range (IQR) is a statistical measure of the middle values of a sample data set that is separated into four equal parts. This middle-value grouping can provide a median range between the upper half and lower half of the data you've collected, allowing you to ignore extreme values.
By Mitch Ryan
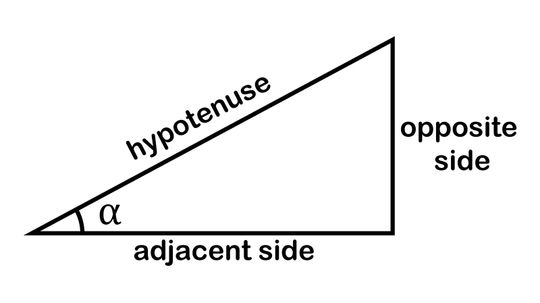
The mnemonic device SOHCAHTOA helps budding mathematicians remember the trigonometric functions sine (sin), cosine (cos) and tangent (tan), which they need to solve for triangles' missing sides and angles.
By Marie Look
Advertisement
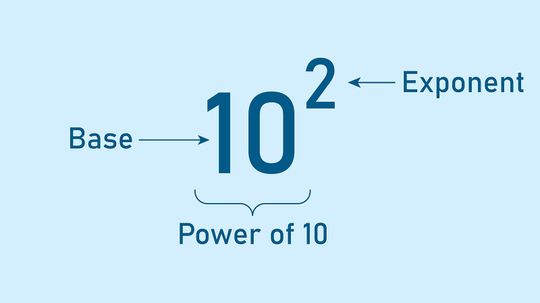
When you're dealing with exponents, numbers can get very big (or very small) very quickly. Therefore, it's helpful to have some short cuts.
By Zach Taras
Absolute value is a mathematical concept often used in conjunction with a number line or graph to represent the relative value from zero (modulus). To illustrate this idea in a different way, the absolute value of a number can be closely related to distance in the physical world.
By Mitch Ryan