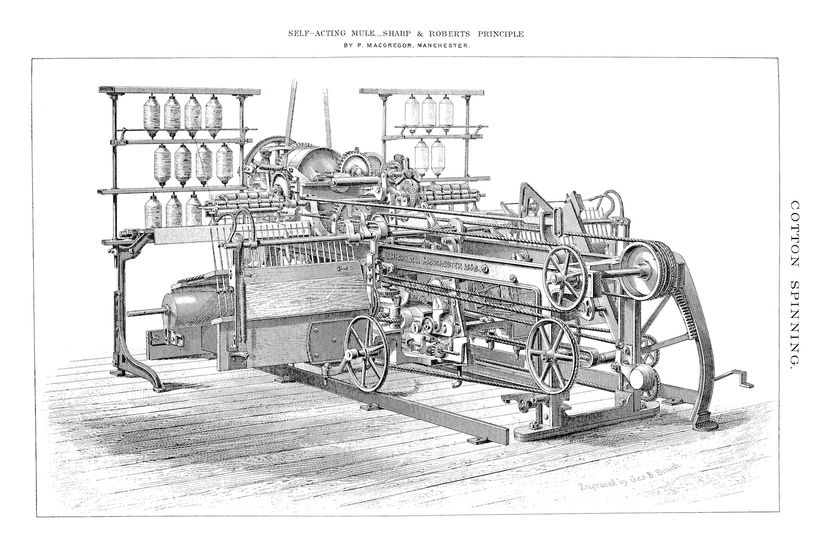
We can't overstate the spinning mule's impact on the textile industry and society as a whole. It fueled the mass production of yarns and textiles, leading to the establishment of large-scale factories and the rise of industrialization. Previously, textile production was predominantly carried out in cottage industries, where hand-operated machines limited output. The spinning mule, with its ability to produce high-quality yarns in large quantities, became a catalyst for the transformation of the industry.
The rapid growth of textile factories, particularly in cotton manufacturing regions like Lancashire, resulted in the migration of workers from rural areas to urban centers. This shift in population dynamics and the concentration of labor in industrial hubs contributed to the formation of bustling cities. Manchester, in particular, emerged as a textile manufacturing powerhouse.
The early spinning mule — and improved versions — turned the textile industry on its head with its ability to produce finer, stronger yarns in large quantities. The subsequent reliance on textile factories and mass production and facilitated socioeconomic changes that characterized the Industrial Revolution.
This article was created in conjunction with AI technology, then fact-checked and edited by a HowStuffWorks editor.