The Revolver
The first revolvers used gunpowder, balls and caps like the earlier percussion-cap pistols. The shooter would load each of the six chambers in the cylinder with gunpowder and a projectile, and place separate percussion caps on corresponding nipples. While the loading procedure was tedious, a shooter could have six rounds fully prepared ahead of time.
In the 1870s, these models were replaced by revolvers that used bullet cartridges instead of gunpowder and caps. Cartridges are a combination of a projectile (the bullet), a propellant (gunpowder, for example) and a primer (the explosive cap), all contained in one metal package.
Advertisement
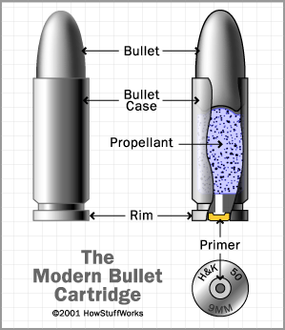
In a modern revolver, cartridges are loaded into six chambers, each of which can be positioned in front of the gun's barrel. A spring-loaded hammer is positioned on the other side of the cylinder, in line with the barrel. The basic idea of the gun is to cock the hammer back, line up a new cartridge in between the hammer and the barrel and then release the hammer by pulling a trigger. The spring throws the hammer forward so it hits the primer. The primer explodes, igniting the propellant, which drives the bullet down the barrel.
The inside of the barrel is lined with spiraling grooves, which spin the bullet to give it stability. A longer barrel improves stability, since it spins the bullet for longer. Extending the barrel also increases the speed of the bullet, since the gas pressure accelerates the bullet for a longer period of time.
In early revolvers, a shooter had to pull the hammer back before each shot and then pull the trigger to release the hammer. In modern revolvers, simply pulling the trigger will force the hammer backward and then release it.
The sequence of events in each shot is very simple:
- The trigger lever pushes the hammer backward.
- As it moves backward, the hammer compresses a metal spring in the gun stock (the handle). The diagram above shows a coiled spring; uncoiled tension springs are also used in revolvers.
- At the same time, a pawl attached to the trigger pushes on a ratchet to rotate the cylinder. This positions the next breech chamber in front of the gun barrel.
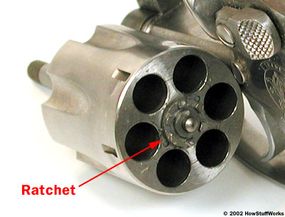
- Another pawl lodges in a small depression on the cylinder. This stops the cylinder in a particular position so it is perfectly lined up with the barrel.
- When the trigger lever is pushed all the way back, it releases the hammer.
- The compressed spring drives the hammer forward. The firing pin on the hammer extends through the body of the gun and hits the primer. The primer explodes, igniting the propellant.

- The propellant burns, releasing a large volume of gas. The gas pressure drives the bullet down the barrel. The gas pressure also causes the cartridge case to expand, temporarily sealing the breech. All of the expanding gas pushes forward rather than backward.
- To reload the gun, the shooter swings the cylinder out and pushes on the ejector rod to operate the extractor in the middle of the cylinder. The extractor grabs the base of the spent shells and removes them from the cylinders.
- To reload, the shooter can place individual cartridges into the chambers or load six at once with a speed loader (basically, a small metal holder with cartridges secured in the right position).
In double-action revolvers, the shooter can either pull the trigger to cock and fire or pull the hammer back ahead of time. The advantage of cocking the hammer first is that the trigger moves more easily when it is time to fire.
Obviously, a revolver is easier to use than a flintlock or a percussion-cap weapon. A shooter can load six shots at a time and only needs to pull the trigger to fire. But revolvers seem very limited next to newer technologies: The shooter must pull the trigger for every shot and stop to reload regularly. On the battlefield, the revolver can't possibly stand up to modern automatic weapons.
The enduring popularity of revolvers is due to the simplicity of their design. Everything fits together so well that the guns very rarely jam. And since they are made with a relatively small number of parts, they are relatively inexpensive to manufacture. For the home defender and criminals alike, it is an ideal, affordable weapon.
For more information on revolvers and other weapons, check out the links below.
