Electricity and Atomic Structure
Toward the end of the 19th century, science was barreling along at an impressive pace. Automobiles and aircraft were on the verge of changing the way the world moved, and electric power was steadily making its way into more and more homes. Yet even scientists of the day still viewed electricity as something vaguely mystical. It wasn't until 1897 that scientists discovered the existence of electrons -- and this is where the modern era of electricity starts.
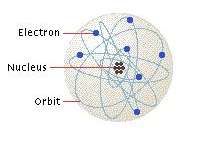
Matter, as you probably know, is composed of atoms. Break something down to small enough pieces and you wind up with a nucleus orbited by one or more electrons, each with a negative charge. In many materials, the electrons are tightly bound to the atoms. Wood, glass, plastic, ceramic, air, cotton -- these are all examples of materials in which electrons stick with their atoms. Because these atoms are so reluctant to share electrons, these materials can't conduct electricity very well, if at all. These materials are electrical insulators.
Advertisement
Most metals, however, have electrons that can detach from their atoms and zip around. These are called free electrons. The loose electrons make it easy for electricity to flow through these materials, so they're known as electrical conductors. They conduct electricity. The moving electrons transmit electrical energy from one point to another.
Some of us at HowStuffWorks.com like to think of atoms as pet dogs and electrons as a case of fleas. Dogs that lived inside or within a fenced-in area, thereby keeping those pesky fleas contained, would be the equivalent of an electrical insulator. Free-roaming mutts, however, would be electrical conductors. If you had one neighborhood of indoor, pampered pugs and one neighborhood of unfenced basset hounds running wild, which group do you think could spread an outbreak of fleas the fastest?
So, electricity needs a conductor in order to move. There also has to be something to make the electricity flow from one point to another through the conductor. One way to get electricity flowing is to use a generator.