To witness the incredible power of steam, you don't have to look any further than the eruption of geysers or the explosion of gasses that occurs when lava reaches the ocean. Early man witnessed such sights and has long sought to control the raw power of steam through technology ranging from the basic tea kettle to the steam locomotive to the modern nuclear power plant.
Regardless of the level of technology involved, steam power comes down to one basic principle: When water heats up to the point of vaporizing, the vaporized water takes up more space than the liquid water did. This is because solids, liquids and gases are each held together by different levels of molecular forces. In solids, the molecules are compact. In liquids, they're further apart. And in gases like steam they're even further apart.
Advertisement
If you heat a can of soup in a fire, the liquid contents will vaporize and eventually expand to the point where the can will explode to release the pressure inside. When this pressure is used to perform a particular task — like turning a turbine or causing a kettle to whistle — steam technology is harnessing steam power. The methods of heating, containing, channeling and using steam have changed, but the basic principle remains the same.
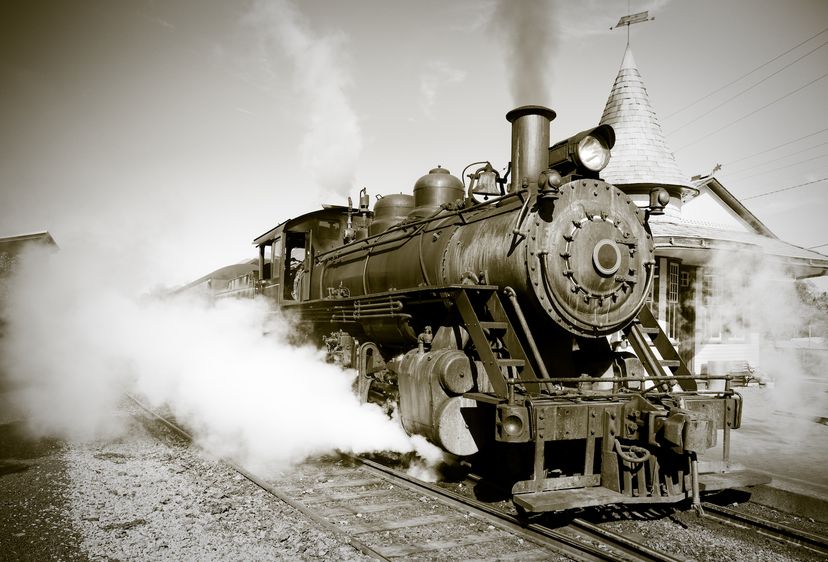
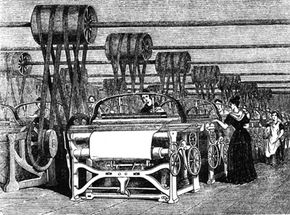
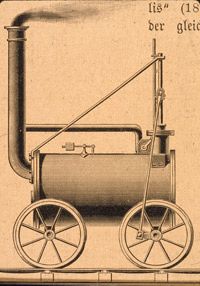
Learning to harness the power of steam has been a long process. Greek mathematician Hero theorized the use of steam technology in the second half of the first century. However, it would be well over 1,600 years before the first practical steam engine came about, leading the way for the invention of the steam locomotive. Powered by steam engines, these locomotives harnessed the energy of steam to propel trains across vast distances.
Advertisement