
For centuries, humankind has looked to the stars for inspiration and guidance. These pictures will show you how to spot several constellations, the basis of modern navigation and astronomy.
Advertisement

Sailors and travelers have long used constellation maps like this one to find their way. Next, find out how the constellations can lead you to true north.
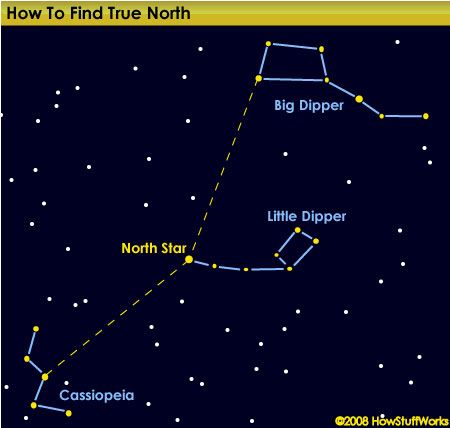
If you live in the Northern Hemisphere, the North Star, or Polaris, guides you true north. You can find Polaris by first locating the Big Dipper and Little Dipper constellations. Polaris is also the middle star in the 'M'-shaped neighboring constellation, Cassiopeia. Next we'll learn how to navigate south.
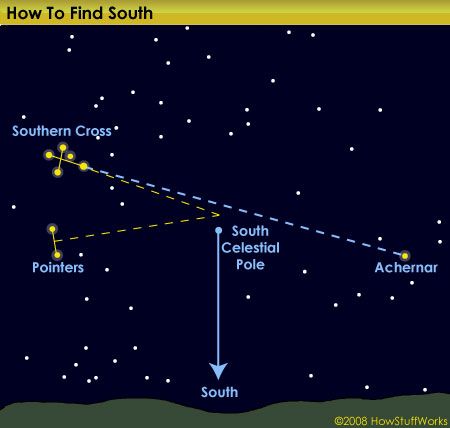
In the Southern Hemisphere, the Southern Cross constellation helps to point you to south. See how this map compares to reality in the next photo.
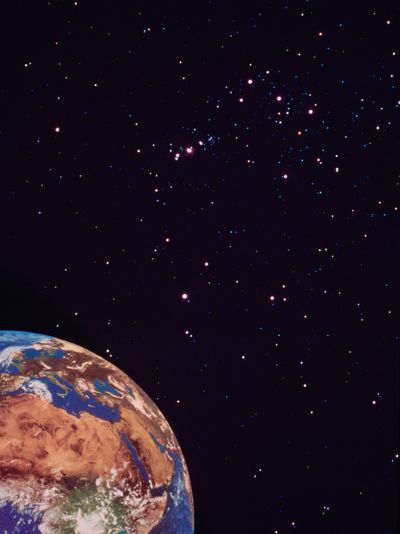

Here's planet Earth accompanied by the Orion constellation. Can't see it? The next picture will help.
Advertisement
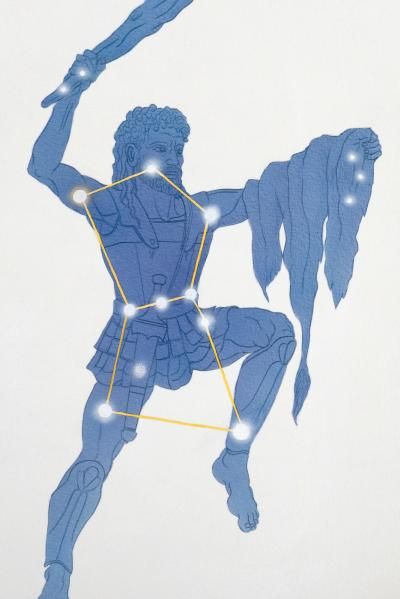

The ancients named this group of stars after Orion the Hunter. See another view of Orion in the night sky next.

Here's the constellation Orion as seen from the space shuttle Endeavour. Next, see another space object intermingled in this constellation.

The Horsehead Nebula is a dark, easily visible nebula in the constellation Orion. See Cassiopeia and Perseus next.
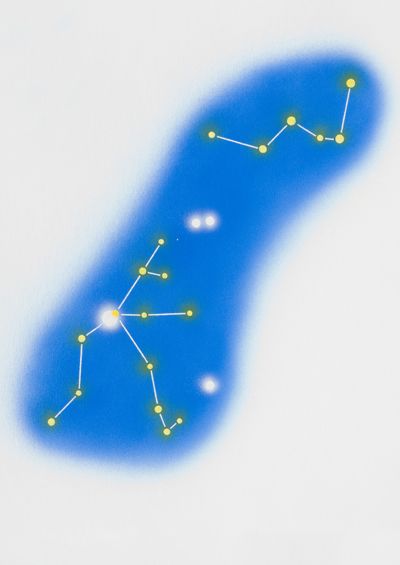
This diagram shows the main stars in the Cassiopeia and Perseus constellations. Next, see Cassiopeia's mythological namesake.
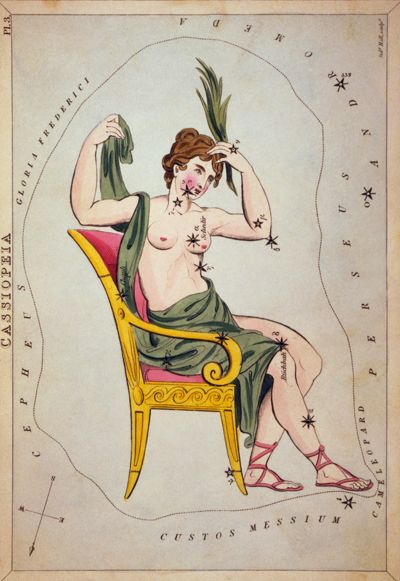
A constellation card of queen Cassiopeia, with holes to allow light through where the stars of the constellation appear. Can you find Cassiopeia's main stars in the sky?
Advertisement
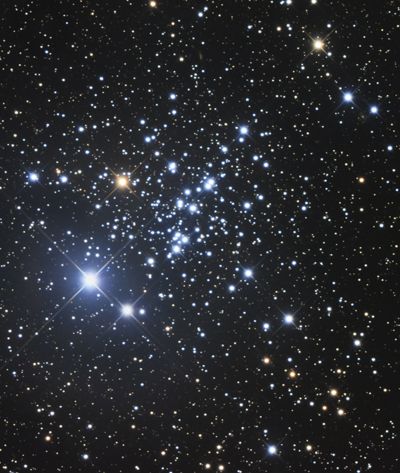

Cassiopeia contains nearly 100 stars and lies more than 9,000 light-years away from the sun. Next, see an exoplanet that may be located within the constellation.

Scientists think the exoplanet HD 7924 b is lurking in the constellation Cassiopeia. Check out Ursa Major next.
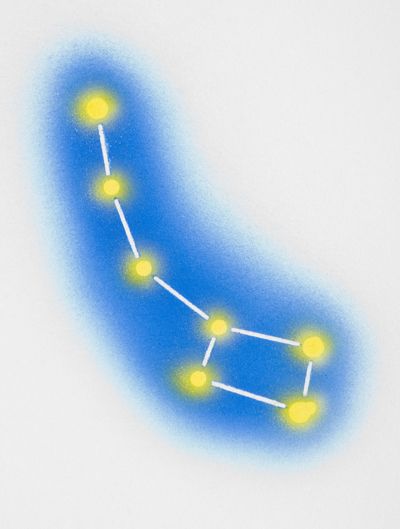
Also known as the Big Dipper, these are the main stars that form the top end of Ursa Major, or Big Bear. See what it looks like in the next image.
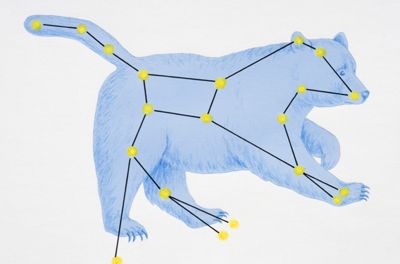
This diagram illustrates the constellation of Ursa Major, complete with the bear's image. On the next page, see one of the constellations that inspired the zodiac calendar.

Sagittarius is a symbol of the zodiac, represented by a centaur archer. Here, the Lagoon Nebula appears in the Sagittarius constellation. See Aquarius next.
Advertisement

Another zodiac symbol, the constellation Aquarius also contains the Helix Nebula. The beloved nebula is a favorite of astronomers and is sometimes dubbed "The Eye of God."

The sprawling constellation Virgo is one of the largest in the nighttime sky, and Spica is the constellation's brightest star. Here, Virgo's Sombrero Galaxy is shown. Next, see the constellation Taurus.

The constellation Taurus features the Crab Nebula. Next, see some of the lesser-known constellations.

Lyra is a small constellation, often represented as an eagle carrying a lyre.

The constellation Auriga is shaped like the helmet of a chariot rider.
Advertisement

Cepheus was named after a king from Greek mythology. Cassiopeia was his queen.

The constellation Cygnus, meaning "swan," includes the group of stars known as the Northern Cross.
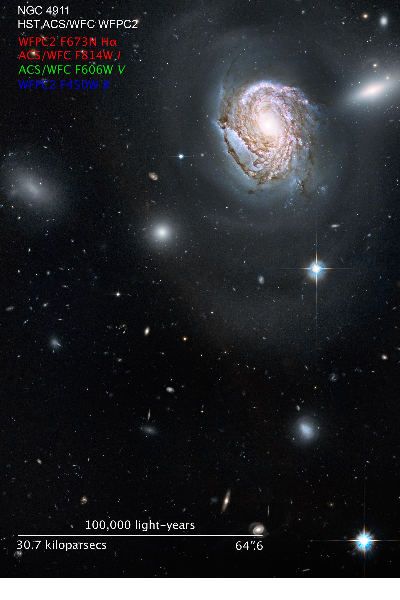

The northern constellation Coma Berenices is one of the few named for a historical figure -- Queen Berenice II of Egypt.

Constellations are made up of individual stars. Of course, you know that our sun is a star, too. How do these objects form?
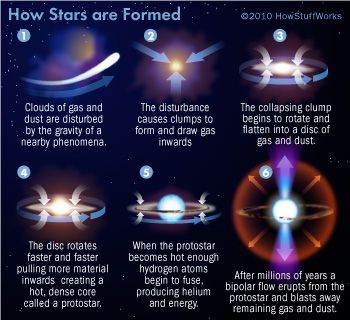
Want to learn more about the stars that form constellations? Read more in How Stars Work.
Advertisement