
Nuclear power provides electricity for a significant percentage of the world's population. This nuclear power plant is located near Dukovany, Czech Republic. Check out the following pages for more pictures of nuclear power plants.
Advertisement

A truck coasts under the shadows of cooling towers at the nuclear power station near Temelin, Czech Republic. Though the plant provides relatively clean power, its construction caused a stir. On the following pages, learn more about nuclear power.

Nuclear power does not depend on fossil fuels, and CO₂ emissions are minimal. Next, learn what technology nuclear power plants use to produce energy.

Steam is no remnant of the Industrial Revolution. Even nuclear power plants employ steam technology. Learn how a nuclear plant produces electricity on the next page.
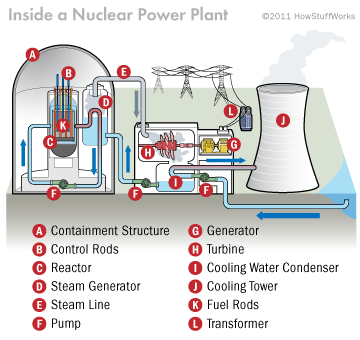
The nuclear reactor is the heart of a nuclear power plant. For more information about the science behind nuclear reactors, take a tour inside a nuclear power plant. On the next page, learn about containment buildings.
Advertisement

As you can tell by looking at this photograph of Germany's Brokdorf nuclear plant, concrete plays an important role in containing radioactive materials.

Nuclear containment helps prevent catastrophic events like the accident at Chernobyl. On the next page, see what protects the nuclear reactor.

This containment building houses the nuclear reactor. Find out why containment buildings are made of concrete on the next page.

The concrete of the containment building keeps the radiation from escaping. Next, see how steam is transported from the reactor.

These pipes carry the steam from the reactor that is used to produce electricity. On the next page, see what goes on in the control room.
Advertisement

The control room monitors every single aspect of the nuclear reactor. On the next page you can see a nuclear power plant's most familiar features.

The cooling towers of a nuclear power plant safely release the steam produced by the plant. See more cooling towers on the next page.

Pictured are two cooling towers of a nuclear power plant. The domed containment building for the reactor can be seen on the right. Glimpse an amazing picture of a nuclear plant at night.

Behold a nuclear plant at night. Next, learn about the disadvantages of this technology.

Nuclear power is generally considered an environmentally-friendly option for producing electricity. Of course, the energy source does have its risks. On the next few pages, you'll learn about three famous nuclear power plant accidents.
Advertisement

The Three Mile Island nuclear plant was the site of a major accident in 1979. Find out what happened next.

In 1979, the reactor core on Three Mile Island went through a partial meltdown. Learn about the cause of this accident on the next page.

A failure in the cooling system at Three Mile Island resulted in a significant release of radioactivity into the area surrounding the plant. On the next page, you can see pictures of the worst nuclear accident in history.

On April 26, 1986, reactor 4 of the Chernobyl power plant exploded. The explosion released a massive amount of radiation into the atmosphere. This concrete structure was built to contain the radiation. Learn more about this aftereffects of this disaster next.
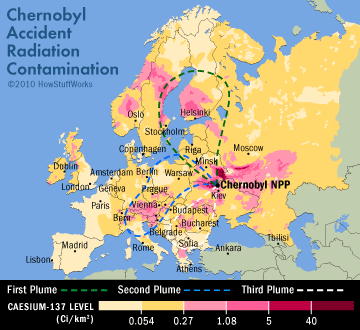
This map shows the levels of radiation in surrounding areas after the Chernobyl accident. Next, see pictures of the devastation.
Advertisement

Thousands of people in the surrounding towns were forced to abandon their homes after the explosion at the Chernobyl power plant. See more of these abandoned towns next.

A classroom sits abandoned decades after the Chernobyl disaster. It will be several decades more before people will be able to inhabit the area again.

An earthquake measuring 8.9 on the Richter scale hit the northeast coast of Japan on March 11, 2011, causing damage to the Fukushima II Dai Ni nuclear power plant.

Pedestrians in Japan wear masks in an attempt to protect themselves from radiation. Next, find out how you can learn more.

Despite past incidents, nuclear power remains an important source of energy for countries around the world. For more information, read How Nuclear Power Works.
Advertisement