Amnesia Detection and Prevention
For Clive Wearing, it all started with a headache. A couple of days later, he couldn't remember his daughter's name. A week later, the downhill spiral began in earnest as the herpes encephalitis started to destroy his short- and long-term memories. Although amnesia may seem to be an obvious disease, if it results from a viral infection, there are specific symptoms to watch out for.
According to the Mayo Clinic, people suspected of having neurological amnesia are screened for the following:
Advertisement
- Whether they can form new memories
- Their ability to recall past events
- Imaginary events told as fact, also called confabulations
- Uncoordinated movements or tremors
- Confusion and disorientation
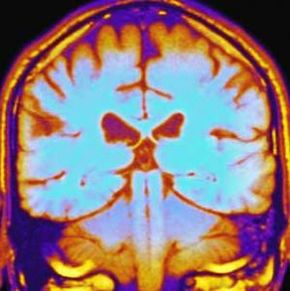
Verbal questioning can be helpful for an initial evaluation, but brain-imaging technology is also beneficial, particularly for people who have had brain injuries. MRIs and CAT scans can reveal parts of the brain that may be contributing to the symptoms of amnesia.
Since neurological amnesia stems from a brain injury, there are a few precautions you take in your daily life. One, wear a helmet when riding a bicycle or motorcycle to protect your head. Two, drink alcoholic beverages in moderation to avoid amnesia caused by alcohol abuse. Finally, for conditions that can trigger amnesia, such as stroke and lack of oxygen or blood to the brain, see your doctor immediately.
Neurological amnesia can also be a symptom of something else. Early signs of amnesia could act as a precursor to Alzheimer's Disease or mild cognitive impairment. Both are forms of dementia, which produces memory loss along with the loss of cognitive skills. Dissociative amnesia can also point to dissociative disorders. Although dissociative amnesia is often temporary, it could be linked to something more serious, such as multiple personality disorder in which people seem to take on alternate identities when triggered by stress.
Next, we'll look at where and why this life-altering condition holds an enduring place in popular culture.