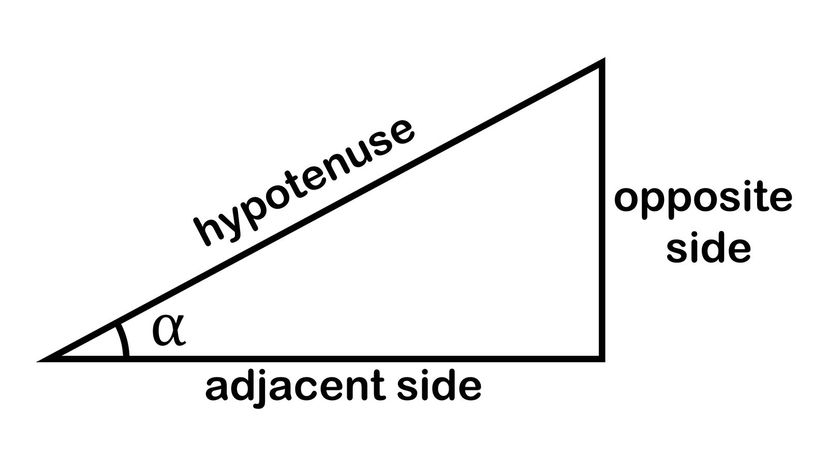
Mathematicians have to calculate the unknown side lengths or angles in a right triangle all the time. To do this, they apply the trigonometric functions.
For example, if you know the value of angle θ, you can find the two sides of a right-angled triangle.
Trigonometric Function Example
Suppose you have a right triangle with:
- Angle θ = 30 degrees
- Adjacent side = a = 5
You want to find the length of the opposite side b.
The tangent of an angle in a right-angled triangle is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side, so:
tan(θ) = opposite/adjacent
You know that:
- θ = 30
- Adjacent side a = 5
So, using the tangent function looks like this:
You know from trigonometric tables or by using a calculator that:
So:
Now, to find b:
The length of the opposite side b is approximately 2.885 units.