Key Takeaways
- While Mount Everest is the highest mountain above sea level, Mauna Kea is technically the tallest when including its underwater portion.
- Contrary to the belief that most body heat is lost through the head, heat loss is proportional across the body surface area.
- Despite popular belief, the Great Wall of China is not uniquely visible from space with the naked eye; other human structures and city lights are more discernible from orbit.
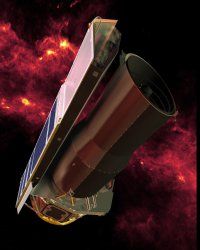
This may not have hit your radar when it happened, and even if it did, you might not have given it a second thought. But we did, my friend, we did. In 2005, the Spitzer Space Telescope (launched in 2003) beamed back conclusive proof that the Milky Way isn't the simple spiral galaxy you've seen illustrated your whole life. It's really a barred spiral galaxy. So instead of elegant arms coiling out from a central sphere, there's a big fat bar across the middle, and the arms of our galaxy sprout from either end.
Now, scientists had been debating this possibility and trying to come up with decisive proof one way or the other for years. And when they did – not much happened. Some mainstream news outlets gave it a little airtime, and the astronomy community talked it up for a while. Once the space devotees all knew about it, everyone else continued on in blissful ignorance, not knowing they were imagining the galaxy they lived in all wrong.
Advertisement
From geography to physiology, there are many examples of people collectively doing it wrong by learning fiction as truth. Here are 10 of the biggest errors walking around masquerading as well-known facts.