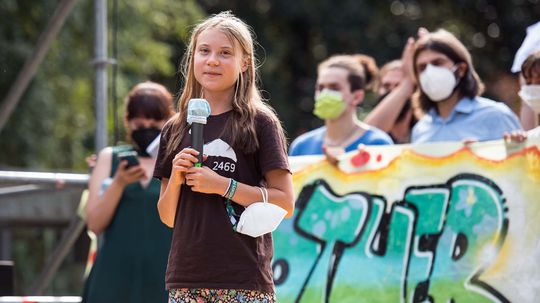Conservation Issues
Conservation issues are a growing concern for most scientists. As humans continue to consume natural resources, many organisms are headed for extinction. Conservation issues include the protection of trees, animals and wetlands.
Learn More
The Euphrates River is one of the most important water systems in recorded history.
By Mitch Ryan
After 2035 it will be extremely unlikely we can stop Earth's temperature from rising enough to kick off a dangerous medley of global disasters.
With the world's population expanding and its arable land shrinking, how in the world are we going to have enough food to feed everyone? Here are five ways.
Advertisement
Insects and biodiversity go hand in hand. Without insects our planet would not survive as they are essential to biodiversity. Check out this gallery on the relationship between insects and biodiversity.
Biodiversity means rainforests and reefs teeming with species right? There's more to it than that though. Genetic diversity has a big role to play, too. Just ask that cheetah cub.
You've probably been spending your summers visiting a barrier island or two and you don't even know it! From Atlantic City to Miami Beach barrier islands are popular vacation spots and amazing ecosystems. Go exploring.
Another series of rolling blackouts are hitting California. Learn why this is happening and how it affects you.
By Kevin Bonsor
Advertisement
Tropical rainforests are the most diverse ecosystems on Earth, and also the oldest. Today, tropical rainforests cover only 6 percent of the Earth's ground surface, but they are home to over half of the planet's plant and animal species.
By Tom Harris
Ever wondered where all that rain goes after a storm? Most of it is absorbed by soil and plants, while watersheds carry the rest into nearby lakes and rivers.
Vertical farming is a method of large-scale farming in an urban environment. Learn about the benefits of a vertical farm and vertical farming technology.
The Sierra Club lobbies for environmental preservation and engages members in fun wilderness excursions.
By Sarah Dowdey
Advertisement
The waste collectors threw your recyclables into one big bin on their truck. How do you know your recyclables are being recycled? And what happens to them next?
By Josh Clark
The Georgia Aquarium is the world's largest aquarium. How did they build habitats for all the animals, and what does it take to keep them fed and healthy? Find out about the aquarium and learn about the animals that call it home.
Without its keystone, a Roman aqueduct collapses. Does the same travesty befall an ecosystem when a keystone species goes missing from the ecological equation?
Critics warn that cryptocurrency networks, whose computers use enormous amounts of electricity to verify transactions, could be a factor in warming the planet. The industry is working to change that.
Advertisement
In the lead-up to U.N. Climate Change Conference, the Swedish activist talked about Biden's climate plan, the media's responsibility and what gives her hope.
If it takes $1 million a year to save the California condor, how much would it take to save every endangered species? Is it possible, and how can we save species we don't even know exist?
Our planet would be a much different place without its richly diverse ecosystems full of plants, animals and microorganisms. What poses the biggest danger to the millions of species that call Earth home?
Plastic may be the longest-lasting legacy of human beings on this planet. But there are lots of ways, big and small, that we can all stop using it. Today.
Advertisement
As the world becomes more urbanized, the demand for sand, a key ingredient of concrete, keeps growing. But there's only so much sand to go around.
By Dave Roos
New findings about ancient, extinct Australasian bandicoot and bilby species underscore how dire things are today when even survivors like these are struggling.
The OneLessStraw campaign encourages people to kick their straw habit to keep plastic from harming the environment.
Helium balloons are dangerous to the environment and wildlife - so why isn't releasing them illegal?
Advertisement
A growing network of global activists is taking an alternative approach to saving the environment: Pushing to recognize natural ecosystems as having legal rights like humans.
It's been 51 years since the first Earth Day, and while progress has been made in some areas, humanity still has had a major impact on the planet.