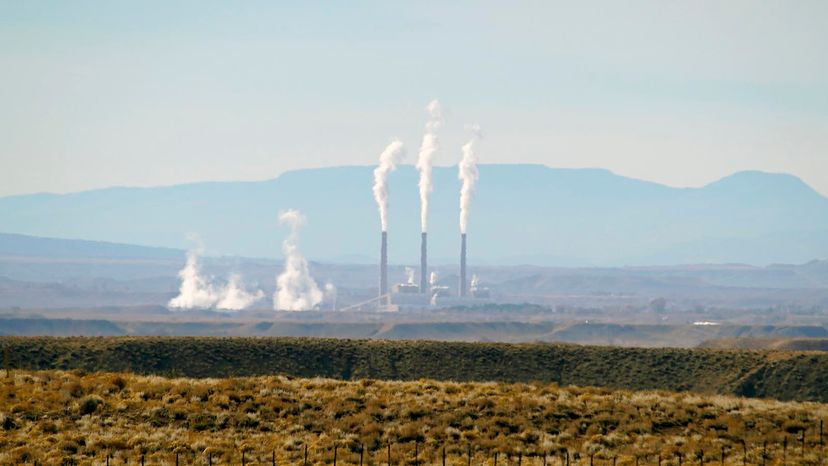
Imagine a scenario where an evil super-genius finds a way to suck all the oxygen out of the air, then buries it in the ground. Sounds like the stuff of comic books? Well, yes, if we're talking about oxygen. But scientists are working on a way to do just that with carbon dioxide. Why capture carbon dioxide from the air? To combat global warming and climate change.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a natural gas that allows sunlight to reach the Earth but also prevents some of the sun's heat from radiating back into space, thus warming the planet. Scientists call this warming the greenhouse effect. When this effect occurs naturally, it warms the Earth enough to sustain life. In fact, if we had no greenhouse effect, the planet's average surface temperature would be just 0 degrees Fahrenheit (-18 degrees Celsius) [source: Lang]. Sure, the skiing might be great, but we'd all be too dead to enjoy it.
Advertisement
Yes, carbon dioxide and the greenhouse effect are necessary for life on Earth to survive. But human inventions designed to burn fossil fuels, such as power plants and transportation vehicles, are releasing extra CO2 in huge quantities. And that's not good.
The decade of 2011 through 2020 was the warmest one on record [source: World Meteorological Organization]. Since the late 1800s, our planet's average temperature has climbed by roughly 2.12 degrees Fahrenheit (1.18 degrees Celsius) [source: NASA]. As a result, ice at both poles is melting, sea levels are rising, animals are changing their migration patterns, and many places have seen an uptick in extreme weather events [sources: Carrington, NOAA and Bradford].
So what's the main driving force behind this warming trend? Unfortunately, humans. Between 1970 and 2004, carbon dioxide emissions rose by 90 percent [source: PBL]. And in 2019, the global average concentration of CO2 within the Earth's atmosphere was higher than it had been at any point in the previous 800,000 years [source: Lindsey].
Recently, the United Nations' Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) called for the wide-scale deployment of carbon capture technology [source: U.N. News].
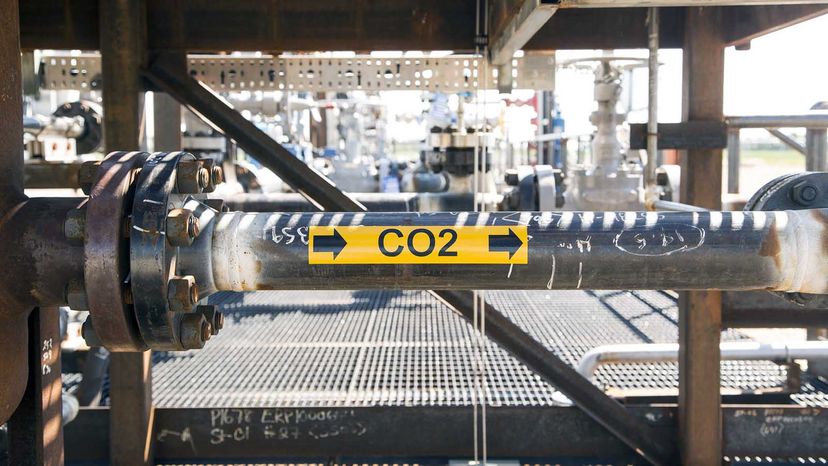
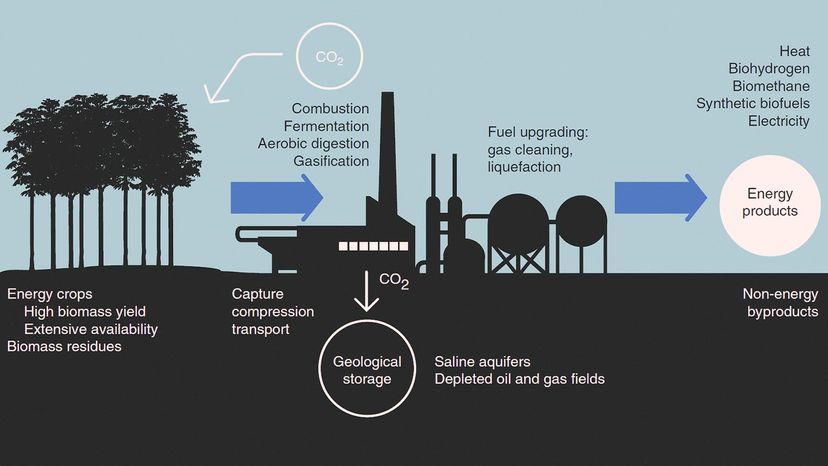
Carbon capture involves trapping the carbon dioxide at its emission source, transporting it to a storage location (usually deep underground) and isolating it. This means we could potentially block excess CO2 from entering the atmosphere.
In this article, we'll look at some of the existing and emerging carbon capture and storage methods.
Advertisement