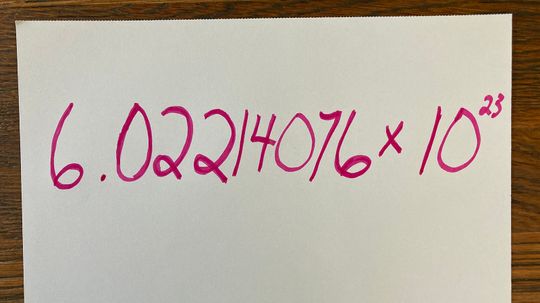Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter and the changes it undergoes during chemical reactions. In this section, learn about everyday chemistry, from chlorine beach to helium, and even why chocolate turns gray.

The Most Expensive Metal in the World Isn't Gold or Platinum

It's Elementary: The Periodic Table Quiz
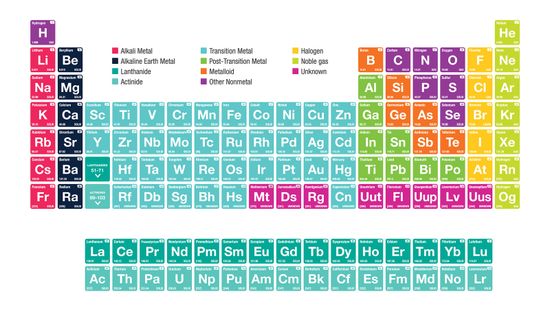
Alkali Metals: Elements in the First Column of the Periodic Table

7 Types of Alcohol for Drinking, Cleaning and More

Understanding the Empirical Formula in Chemistry
Strong Bases: Properties, Applications and Examples

Delta-8 vs. Delta-9: Comparing Types of THC

What Color Is the Hottest Flame?

Why Do Bubbles Pop?
Learn More / Page 2
Imagine spending your days racked with pain or losing pound upon pound because nausea leaves you unable to eat. Now imagine that someone offers you a wonder drug to cure all your ills. The problem? It's illegal.
We love it. We wear it glittering around our necks and sparkling at our ears, wrists and feet. We pass it down to our children and hoard it in secret stashes. Why is this precious metal so prized?
Can you pass the acid test? That electric Kool-Aid changed the fabric of 1960's American counterculture. So, what's it's like to trip on LSD?
Advertisement
Mushrooms - they're not just a pizza topping. This psychotropic fungus has guided many an adventurer on a trip. How do shrooms make their magic?
We once emptied the scent pods of male musk deer into a bottle of fragrance and doused it on, feeling like a million bucks. How has perfume changed since then?
It begins with an unassuming "H" and ends in crazy elements that you've likely never heard of. But the periodic table, encapsulated on a mere sheet of paper, can be a scientist's best friend and a testament to our human drive to organize the world.
Mass spectrometry enables the major league to sniff out athletes guilty of doping. It can also help us locate oil or design a killer perfume. Who says chemistry isn't cool?
Advertisement
Once considered a semiprecious metal alongside gold and silver, aluminum pretty much languished in obscurity until the 19th century. How did the metal become so ubiquitous?
When it comes to stimulating the human central nervous system, meth can hold its shaky, toothless head high. Why is this drug so additive?
If the idea of being completely knocked out by a cocktail of drugs while doctors operate on you freaks you out, you're not the only one. But that's not what anesthesia is all about it - and it might scare you less if you understand how it works.
About 90 percent of Americans consume some form of caffeine every day: It's our most popular drug by far. What's so special about this stimulant?
Advertisement
Helium balloons tend to fascinate adults and children alike (and it's not just the Donald Duck voice thing, though that is a big draw). Learn all about helium and why it floats!
Helium is the second lightest element on the Periodic Table. How is helium created?
I recently used chlorine bleach to clean the siding on my house, and I was amazed at how well it worked! What is bleach? How does it remove stains? Is the chlorine in bleach the same as the chlorine in drinking water or in swimming pools? Is chlorine safe to use?
By Yara Simón
Chemical formulas provide a concise explanation for reactions. In this article, we explain the formula for the reaction in a smoke detector.
Advertisement
Most of us have heard the talk about oysters and chocolate, and maybe you've read an article about the stimulating effects of ginseng. But garlic, licorice and cucumber? Learn about the history of aphrodisiacs and whether they've been proven to be effective.
If water is made up of hydrogen and oxygen, why can't we breathe underwater? It has to do with how molecules combine and how the human lung functions.
Ever wondered exactly what they "artificial flavors" in your candy are, and why no specific ingredients are listed? Find out in this article.
Viagra is one of the best-known drugs of all time. Nearly every adult in America has heard of the drug and can tell you what it does. Find out how this high-profile medication works its magic.
Advertisement
First there was Volvo. Then came IKEA. Well get ready for the next major Swedish export: snus, a smokeless tobacco product, similar to dip or chew.
Scientists at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory just made history with einsteinium. They held a sample of the short-lived element long enough to measure some of its chemical properties.
By Dave Roos
From soap to pharmaceutical products, glycerine has many applications.
That's one seriously big number, and technically Amedeo Avogadro didn't even come up with it. So how did the Italian chemist make such an indelible (numerical) mark on the wonderful world of chemistry?
Advertisement
It's a force of habit to shake spray canisters, but when it comes to canned air, that inclination could cause frostbite.
Developed in Israel, this foul-smelling liquid has been used on Palestinian and Israeli protesters - and it's showing up in the United States.
By Sarah Gleim