Science Dictionary
Do you know what a meteor is, or what scientists mean when they are talking about cryogenics? Our collection of science terms explains the meaning of some of the most common scientific ideas.

10 Scientific Words You're Probably Using Wrong

Can a planet float on water?

Can You Nominate Yourself for a Nobel Prize?

How Do You Win a Nobel Prize?

Quiz: How Much Do You Know About Stephen Hawking?

10 Cool Things About Carl Sagan

10 Cool Things About Neil deGrasse Tyson

How do polymer crystals work and why do they absorb so much water?

Is a Karat the Same as a Carat?

4 Quantum Physics Misconceptions, Busted

Chaos Is Not Randomness: A Complex Systems Scientist Explains
Learn More / Page 2
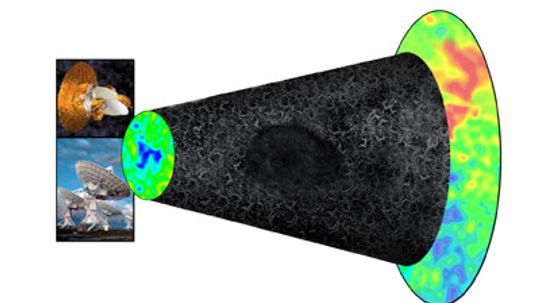
For decades, stargazing scientists have been facing their own darkness on the edge of town as they try to explain one of astronomy's greatest mysteries: dark matter. Have they been successful, or will the universe carry its secrets for a long time?
While routinely scanning the stars, NASA scientists came across something they didn't expect to see: a vast area of space empty of stars, planets and matter.
So much about galaxies remains a mystery. We know what they're made of and that we live in one (the Milky Way), but how many galaxies are in the universe?
Advertisement
How do scientists find details about the early days of our solar system? One way is to investigate comets. Find out how the Deep Impact spacecraft fired an impactor into Comet Tempel 1 to get some answers.
By Carolyn Snare
Scientists announced the discovery of the largest known planet in the universe. TrES-4 has a density similar to balsa wood, and some say this gas giant could float on water. Learn why this planet is so puzzling and how planet hunters make amazing discoveries like these.
What exactly are asteroids? And what was the NEAR Shoemaker mission about?
Polymer crystals are amazing in that they can absorb many times their size. In fact, one pound of these crystal flakes can hold up to 50 gallons of water. Find out what these polymer crystals are and why they are able to absorb so much water.
Advertisement
You've heard of the big bang, of course, but do you have any idea as to what was happening during that massive flurry of activity billions of years ago?
By Robert Lamb
So much of our cosmological history starts with the much-discussed Big Bang, but what led up to that cataclysmic moment? And did time even exist back then?
The world often seems chaotic and events appear to occur randomly, but what's the difference between chaos and randomness?
As much as we might like to think that our collective knowledge has unlocked most of the mysteries of the universe, we've really only got a hold on a tiny fraction of the knowledge required to fully understand it all-and it's a weak hold at best. But every once in a while a new theory [...] The post 12 Of The Most Mind-Blowing Scientific Theories Ever Conceived appeared first on Goliath.
By Wes Walcott
Advertisement
If you have a theory that potato chips are making you fat (with the proof being your expanding waistline), you've just used two scientific terms in a very unscientific way.
By Beth Brindle
He built President Eisenhower an indoor golf-training machine, analyzed the Zapruder film and searched for an Egyptian pyramid's treasure chamber using cosmic rays. Aren't you dying to meet this wide-ranging scientist?
The man who had some theories about relativity was also an eccentric who gleefully eschewed socks, dodged German military service and spurned social conventions.
Frequency has to do with wave speed and wavelength is a measurement of a wave's span. Learn how frequency and wavelength of light are related in this article.
Advertisement
He ventured to the abyss of black holes, wagered on the information paradox and floated around in zero gravity. Meet the man, the legend, the super scientist: Stephen Hawking.
How cool would that be to stand amongst the company of fellow laureates like Mother Teresa or Albert Einstein? We have some ideas for scoring you one.
Scientists are still trying to figure out the essence of dark matter. If they do, will it lead only to greater understanding, or can we develop new technologies?
The late marine biologist Rachel Carson's groundbreaking book, "Silent Spring," debuted 60 years ago as one of the finest works of nature writing ever.
By Oisin Curran
Advertisement
He was born exactly 300 years after Galileo died. He never won a Nobel Prize, although he was awarded a guest spot on "The Simpsons." What else do you know (or not know) about this acclaimed physicist?
By Jane McGrath
Every day, astronomers unravel a little more of the universe's inner workings, but the jury is still out on 95 percent of its contents.
By Robert Lamb
Nobel prizes offer lots of prestige and big payouts. But how do you become eligible for one? And can you lobby for yourself?
By Dave Roos
Planck's constant, which made an appearance in the Netflix series "Stranger Things," is one of the most important differences between reality at the atomic and subatomic level and what we can see around us.
Advertisement
Having one Nobel Prize winner in the family is a huge accomplishment. But the extended Curie family had five winners - and one was even awarded twice. How did they get so smart?
Everyone knows that nothing travels faster than the speed of light, but how does the speed of dark compare? Read on to find out!
By Bambi Turner