Environmental Science
The environment is truly a thing of beauty and should be protected whenever possible. What can we do to save the environment, and what new technology is available to help us?

The Fish Doorbell Isn't a Joke ... Seriously

The Euphrates River, at the 'Cradle of Civilization,' Is Drying Up

Study Says 2035 Is Climate Change Point of No Return
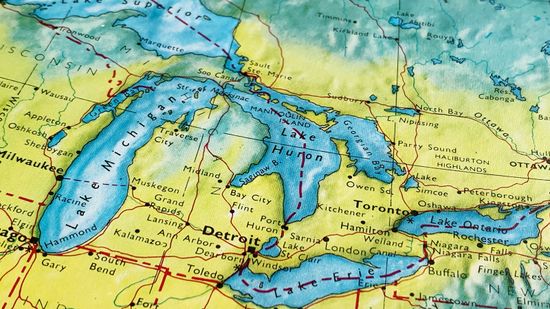
What State Has the Most Lakes in the U.S.?

Devon Island: The Icy Canadian Land That NASA Uses for Mars Research

10 Tundra Plants That Prove Life Finds a Way

How Many Birds Are Killed by Wind Turbines, Really?

How a Lithium Mine Works and Impacts Local Communities

How to Sell Electricity Back to the Grid

The Worst Air Quality in the World Is in Mountainous Terrain

The World Hits 8 Billion People; Is That Good or Bad?

Quiz: Can You Tell Climate Change Fact From Fiction?

6 Most Futuristic Cities Powered by Renewable Energy

Top 5 Green Robots

5 Things to Consider When Building a Solar-powered Home
Learn More / Page 18
If geology has taught us anything about Earth's history, it's that nothing is permanent. And that goes for mountain ranges, all of which are constantly rising and falling.
By Mark Mancini
For centuries, ancient cultures celebrated the winter solstice, the shortest day of the year, as the "day the sun came back." Here are five enlightening facts about the winter solstice.
Scientists from The Ohio State University have drilled longest ice core from outside the poles.
By Mark Mancini
Advertisement
Although the trenched enclosures were probably used to conduct rituals, they can tell us how the ancient indigenous people of the Amazon managed their forests.
The perfectly preserved remains of a 3,000-year-old settlement called Must Farm provide a window into the lives of the Bronze Age Britons.
Rising sea levels, increased flood and extreme heat are all signs of climate change. Cities are trying some innovate strategies to cope with and mitigate these events.
By Dave Roos
Ever wondered what's the difference between a river, a stream, a brook and a tributary?
By Amanda Onion
Advertisement
Getting your home to zero waste doesn't have to mean re-structuring your entire life. Sure, you'll have to make changes, but most of them are surprisingly easy.
By John Donovan
Ocean water is not actually blue, but appears in different shades for many reasons.
By Amanda Onion
The Sahara has expanded by about 10 percent in the past century, mostly due to natural causes, but not all. We can blame the rest on man-made climate change.
Plastic may be the longest-lasting legacy of human beings on this planet. But there are lots of ways, big and small, that we can all stop using it. Today.
Advertisement
Climate change may be melting glaciers, but it's also reducing the oxygen of the world's oceans. Without oxygen, many marine organisms may no longer be able to survive.
As the world becomes more urbanized, the demand for sand, a key ingredient of concrete, keeps growing. But there's only so much sand to go around.
By Dave Roos
Talk about a Brexit! Scientists have clues to catastrophic flooding that destroyed a land bridge that once connected England and France.
New findings about ancient, extinct Australasian bandicoot and bilby species underscore how dire things are today when even survivors like these are struggling.
Advertisement
Most mammals have a penis bone called a baculum, but humans don't. A new study sheds light on the history of the baculum, and why ours is missing.
Now that its sequel is out, where did Al Gore's landmark environmental documentary hit the mark? What did it get wrong?
A new 'atlas' of light pollution finds that one third of people on Earth can't see the night sky's most dramatic feature.
The OneLessStraw campaign encourages people to kick their straw habit to keep plastic from harming the environment.
Advertisement
Science has determined that disappearing completely into quicksand isn't possible - but that doesn't mean that getting stuck still won't kill you.
Surprisingly, living in a city with a high level of natural radiation doesn't have any ill effects.
By Alia Hoyt
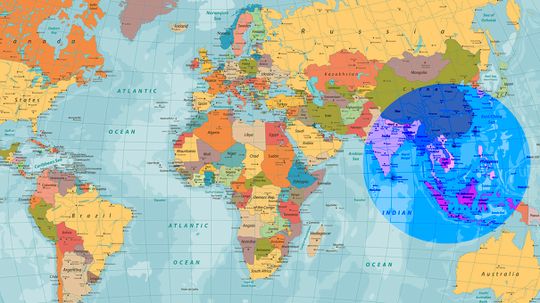
The circle is only 5,000 miles wide.
The Denmark Strait cataract dwarfs every other waterfall in the world, but you can't see it because it's deep under the Atlantic Ocean.
Advertisement
Buckingham Palace announced that Queen Elizabeth II is making changes to the Royals solid-wasted plan, and that includes banning many plastics.
Helium balloons are dangerous to the environment and wildlife - so why isn't releasing them illegal?