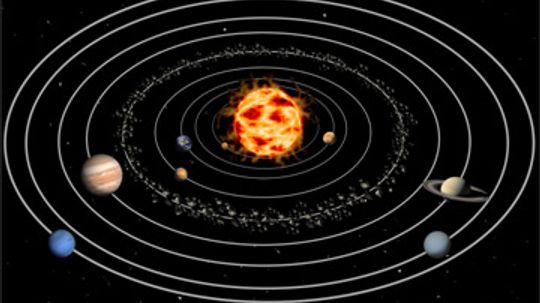
The Solar System
In the Solar System Channel, you can explore the planets and celestial objects around our own sun. Learn about topics such as Mars, Jupiter and the Moon.

88 Constellation Names (and 24 You Can Only See From the Northern Hemisphere)

Constellation Pictures
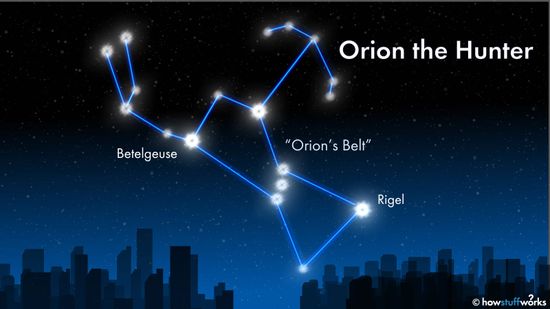
How to Find Orion's Belt in the Night Sky

Radio Telescope Image Gallery

How do I build a telescope at home?

Shooting the Stars as an Astrophotographer

10 Types of Stars Blazing and Collapsing in Our Universe

Solar Storm + Earth's Magnetic Field = Auroras Galore

What's the Brightest Star in the Sky? Depends on the Season
Learn More
When the Sun gets rowdy, Earth feels it. A geomagnetic storm happens when solar activity stirs up Earth’s magnetic field, producing large magnetic disturbances that can mess with everything from navigation systems to power grids.
The harvest moon is the full moon closest to the autumnal equinox, typically in late September or early October in the Northern Hemisphere.
Mercury Retrograde is coming. Is your life about to turn upside down? Discover the dates you must know & how to avoid total disaster.
By HowStuffWorks
Advertisement
Delve into the Earth's layers: crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. Discover the secrets beneath our feet and the dynamic processes at play.
By HowStuffWorks
Explore the mysteries of the outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Dive deep into their atmospheres, moons, and unique phenomena.
By HowStuffWorks
Nothing lasts forever. Does that include our home planet, too?
Sometimes hundreds of people armed with high-tech cameras can make amazing scientific discoveries, as in the case of STEVE.
Advertisement
March's full moon is called the worm moon for an unusual reason. What are some other names for the March moon and when can you see it?
Every 24 hours, Earth makes a full rotation on its axis. But why does Earth spin in the first place?
Researchers at Australian National University studied 5,000 star-eating behemoths to find out.
January's moon is called the wolf moon, but it's also known as the center moon and the freeze up moon (among other names). Here's why.
Advertisement
All of the planets in the solar system are named for Greek gods, except Earth. So where did the name come from?
By Mark Mancini
Why do planets in the solar system all seem to be round? Why not cylindrical? Or even cube-shaped?
By Mark Mancini
In the darkness of space, we're comforted by our moon, the circular inspirer of song lyrics, poetry, and wannabe astronauts. But what do you really know about the moon and its history? Take this quiz to find out.
Those stars twinkling in the nighttime sky may actually be crystal spheres. And our beloved star is headed in that direction, too. Eventually.
Advertisement
A massive planet 10 times the size of Earth seems to have been lurking on the edge of our solar system for some time now. How come we never noticed it before?
Killer asteroids are all fun and games -- until they're headed for Earth. How do we stop cosmic hot potatoes from wiping out our planet?
It's not a pleasant thought, is it? But when you mix chaos theory with a few crazy cosmologists, those tidy, predictable orbits start getting lively.
Sunspots are peculiar dark areas that show up regularly on the surface of the sun -- and often for no reason. What causes them? What effect could these funny little spots have on the Earth?
Advertisement
Hundred of meteors fly across the sky every night, but only a few make it to Earth. Meteors are best known for the brilliant streaks of light they make as they burn up in the atmosphere. Learn about 10 memorable meteor crashes that left an impression.
We know it's not made of green cheese, but what are the origins of the moon? Learn astronomers' theories about where the moon came from.
Why does the moon look so much bigger when it is near the horizon than when it is high up in the sky? This question has been pondered for hundreds if not thousands of years, and is commonly referred to as the moon illusion.
Since the 1960s, we've been captivated by the planet Mars. How different is our neighbor, and what have we learned about the most explored planet?
Advertisement
A total solar eclipse is a rare event that can be an amazing thing to witness. Learn about solar eclipses and how to observe one safely.
Where I live it is pretty common to see "shooting stars" -- streaks of light in the sky at night. How big is a shooting star? Do they land on earth or do they burn up? Do they land on the ground as meteorites?