Cellular & Microscopic Biology
Cellular and microscopic biology allow scientists to study cells and microorganisms. Cellular biology is the study of cells, including their structure and function. Microbiology is the study of microorganisms, which include algae, bacteria, and viruses.
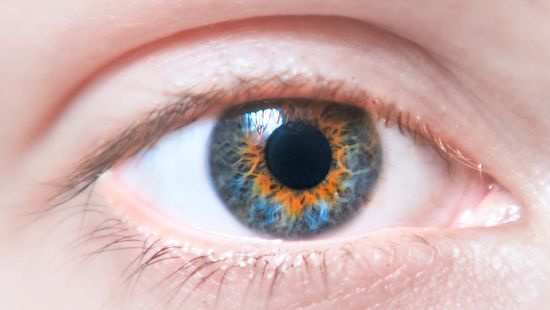
Central Heterochromia: When to Worry About Eye Color

10 Types of Noses to Spot in a Crowd

3 Major Types of Mushrooms: Edible, Wild and Poisonous

3 Types of Trees You'll Find All Over the Planet

A Corpse Flower Can Grow Over 12 Feet (3.7 Meters) Tall

Indica vs. Sativa: How to Distinguish Between Cannabis Plants

Neanderthal vs. Homo Sapien: Separate Species With Different Fates

Howstuffworks Interviews: Extinction Level Events with Annalee Newitz

What will the Earth look like in 50,000 years?

Is a Woolly Mammoth Clone Even Possible?

The Most Common Hair Color Isn't Blonde

What Is the Most Common Eye Color? Over 70% of People Have It

9 Types of Intelligence: The Many Ways to Expand Your Mind
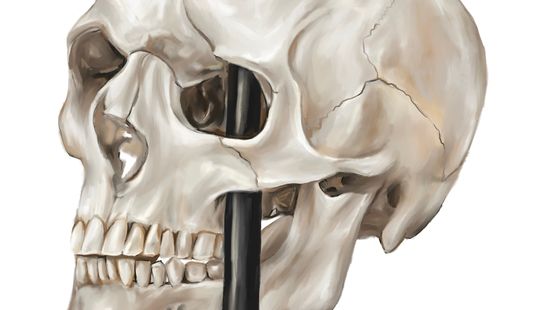
Phineas Gage and the Birth of Modern Neuroscience

Call of the Void: A Counterintuitive Form of Self-preservation
Learn More / Page 3
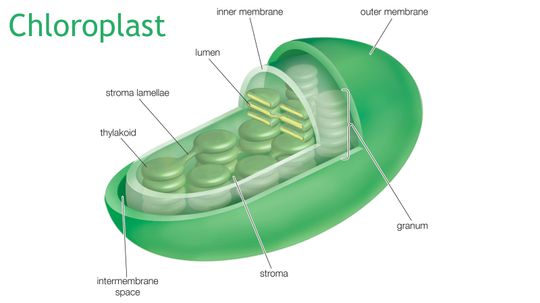
No life, except possibly very small bacteria, would exist on Earth without photosynthesis.
Chloroplasts are where some of the most miraculous chemistry on Earth goes down.
Viruses need hosts to replicate and reproduce. So if a virus has no host, how long can it survive? It depends on a lot of factors.
Advertisement
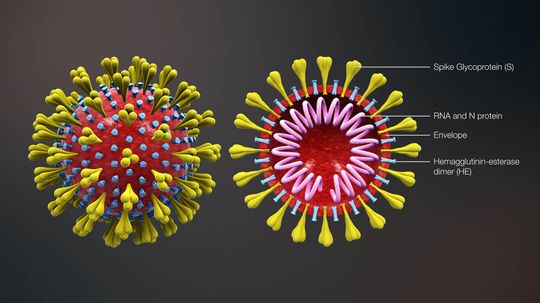
Viruses, viroids and prions are microscopic, infectious particles with a common, despicable goal - but the way each goes about achieving that goal is different.
By Debra Ronca
Your body replaces billions (with a b!) of cells every day. In about 100 days, 30 trillion be replaced, but does that mean you're a new person, too?
You probably use the words mold and mildew interchangeably. But these two types of fungi aren't quite the same. Is one worse?
Herd immunity means that after a certain percentage of a population is immune to a disease, the whole population is. This is usually achieved through vaccination but some are not convinced.
By Alia Hoyt & Molly Edmonds