Cellular & Microscopic Biology
Cellular and microscopic biology allow scientists to study cells and microorganisms. Cellular biology is the study of cells, including their structure and function. Microbiology is the study of microorganisms, which include algae, bacteria, and viruses.
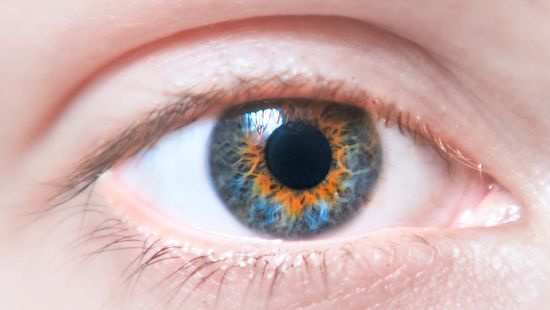
Central Heterochromia: When to Worry About Eye Color

10 Types of Noses to Spot in a Crowd

3 Major Types of Mushrooms: Edible, Wild and Poisonous

3 Types of Trees You'll Find All Over the Planet

A Corpse Flower Can Grow Over 12 Feet (3.7 Meters) Tall

Indica vs. Sativa: How to Distinguish Between Cannabis Plants

Neanderthal vs. Homo Sapien: Separate Species With Different Fates

Howstuffworks Interviews: Extinction Level Events with Annalee Newitz

What will the Earth look like in 50,000 years?

Is a Woolly Mammoth Clone Even Possible?

The Most Common Hair Color Isn't Blonde

What Is the Most Common Eye Color? Over 70% of People Have It

9 Types of Intelligence: The Many Ways to Expand Your Mind
Phineas Gage and the Birth of Modern Neuroscience

Call of the Void: A Counterintuitive Form of Self-preservation
Learn More / Page 2
Nearly every cell in your body has the same DNA. It's the hereditary material located your cells' nucleus. But what does it do and why is it so important to all living beings?
You won't find some of history's biggest killers on this list, but you will find at least one disease that will make you want to bite something and another that might make you break out in "elevated pustules." Curious yet?
By Garth Sundem
Pasteurization is the process of removing harmful pathogens from various types of food. How was this process discovered?
By Carol White
Advertisement
Phone calls, e-mails, sign language, friendly shouts -- this is how we communicate in our daily lives. Bacteria, some of the tiniest organisms on Earth, have a different way of talking.
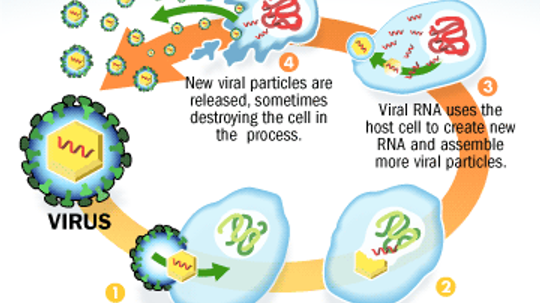
For something too small to be detected by an ordinary microscope, viruses pack a big punch. We all know they can wreak havoc on the body, but how do they do it?
Cell suicide sounds unpleasant, but this programmed cell death is the reason your fingers and toes are no longer webbed. What's the story behind apoptosis, and what does it have to do with curing disease?
Mold is a type of fungus, and it's everywhere - indoors, outdoors and even in the air. But is black mold worse than the rest? Is it as deadly as people say?
Advertisement
The mass of microorganisms swarming inside your favorite elite athlete's body may be a great business opportunity.
By Amanda Onion
While HeLa cells have been star players in medical research for decades, the woman behind them remained in the shadows for years. Discover the amazing story of Henrietta Lacks and her immortal cells in this article.
Biofilms form when single microorganisms attach to a hydrated surface and undergo a "lifestyle switch." But why should we care about biofilms?
Dust traveling over the Atlantic from North Africa feeds both phytoplankton that makes the oxygen we breath and the bacteria that could kill us.
Advertisement
It's all connected! Recent rodent research suggests that immune responses and social behavior may be more intertwined than we realized.
By Julia Layton
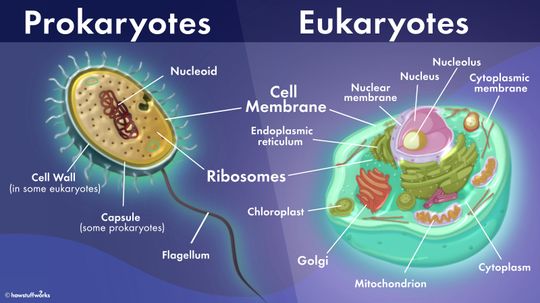
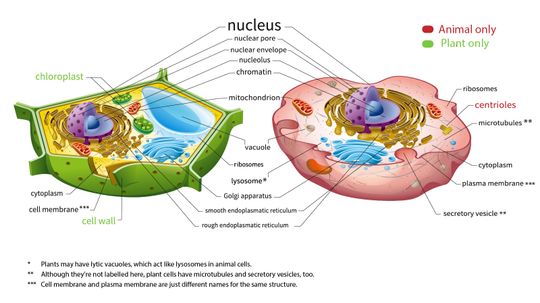
Prokaryotic cells are like single-room efficiency apartments while eukaryotic cells are like mansions with many rooms - and they are the only two kinds of cells in the world.
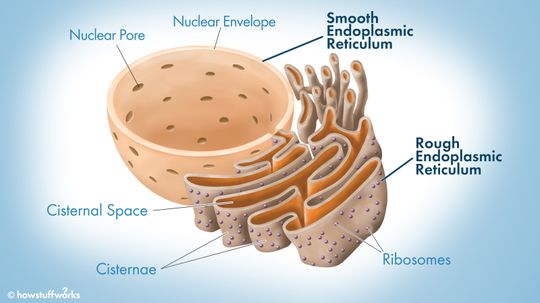
The part of your cells that helps you recover from a hangover is shaped like a maze of tubes and is made of two parts - the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
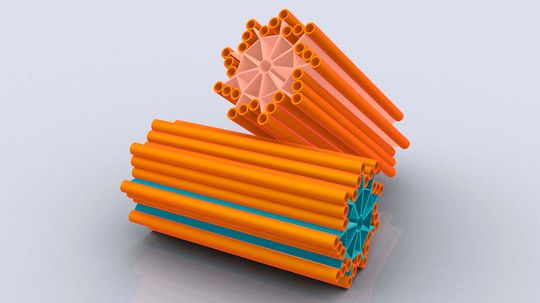
Centrioles are spindles that create the pathways for chromosomes to follow during cell division.
Advertisement
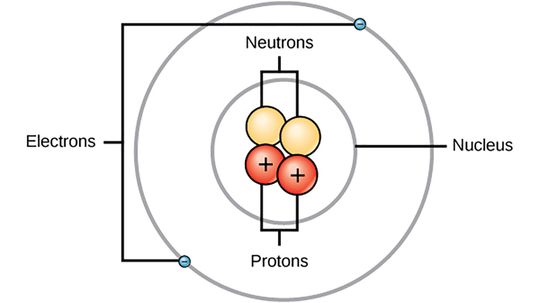
Niels Bohr proposed the model of the atom that we still learn in school today, even though it's technically incorrect.
Researchers are calling for a new "Noah's Ark" to store microbes that might one day be valuable.
By Chris Opfer
Australia's western coast boasts such pink wonders. But what gives these lakes their pink hue?
While researchers can't say from this small study whether hairy men are inherently germier than the rest of the human race, the results are startling.
Advertisement
Scientists started an experiment back in 2014 that will run for 500 years. The first results were recently published. So, what have they found so far?
Scientists have found that ancient fossilized chlorophyll was dark red and purple in its concentrated form, which means that when diluted by water or soil, it would have lent a pink cast to earth and sea.
Bacteria are both friend and foe to humanity. They cause and cure health problems, make rotting food stink and give sourdough its delicious taste. Find out how these countless tiny microbes accomplish all of this and more.
While plant and animal cells are strikingly similar, there are a few key differences.
Advertisement
When an electron loses its partner, it creates a free radical. So is that free radical now potentially hazardous to your health?
Yep, fungi are all around us - in the grocery store, in the woods or living on your discolored toenail. And fungi can break down almost anything.