Astronomy
Astronomy is a broad discipline covering all facets of astrophysics. In this section you can learn about the origins of the universe, black holes and other astronomical phenomena.

88 Constellation Names (and 24 You Can Only See From the Northern Hemisphere)

Constellation Pictures
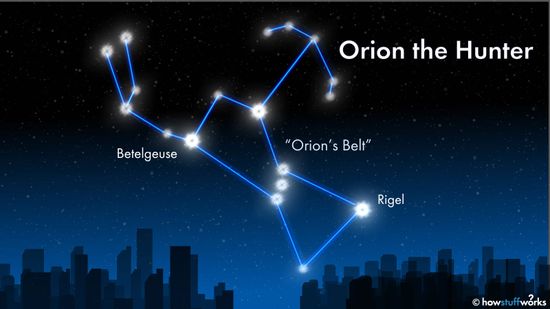
How to Find Orion's Belt in the Night Sky

Radio Telescope Image Gallery

How do I build a telescope at home?

Shooting the Stars as an Astrophotographer

10 Types of Stars Blazing and Collapsing in Our Universe

Solar Storm + Earth's Magnetic Field = Auroras Galore

What's the Brightest Star in the Sky? Depends on the Season
Why a Geomagnetic Storm Makes for Pretty Skies and Tech Scares

What Is a Harvest Moon?

Mercury Retrograde Explained: Dates, Effects, and How to Cope
Learn More / Page 4
Check out this video of what astronauts in space see as the shadow of the moon crosses our planet.
And don't worry. Even if NASA misses, we'll be fine.
Every autumn, Earth passes through a stream of debris left by Halley's comet, resulting in some beautiful nighttime meteor showers called the Orionids. Here's what to watch for.
Advertisement
Get ready for the most powerful electromagnetic explosion the universe has ever known.
The annual Leonid meteor shower is back, and peaks in the late-night hours of November 17. It's made up of tiny bits of debris from the comet Tempel-Tuttle. Here's how to see it.
Neither massive planets nor tiny stars, brown dwarfs are entirely different substellar curiosities that possess qualities of both.
Many people dream of climbing Mount Everest, but what if you could scale the highest mountain in the solar system? That one is more than twice as tall as Everest! So, where is it?
Advertisement
If you imagine the eight major planets in a single line stretching out from the sun, this alignment occurs roughly every 13.4 trillion years. And our solar system is 4.5 billion years old.
Aldebaran is not just the brightest star in the constellation Taurus, it's also the 14th brightest star in the sky.
The Tau Herculids meteor shower was made of debris from the broken comet SW3 and produced a lot of shooting stars, but not quite the meteor shower that was hoped for.
Leash your cheetah, buckle your seatbelt and tell Usain Bolt to take a knee. We're about to power through some of the speediest stuff this universe - both in the real world and in fiction - has to offer.
Advertisement
When a huge star collapses, it releases massive amounts of radiation in concentrated streams. If one of those streams hit Earth, it wouldn't be pretty. But where should we put "gamma-ray bursts" on our list of anxieties?
A billion years ago, the moon stopped being geologically active. But that's not to say that the moon is doing nothing for Earth. Let's find out why we owe our moon some thank yous.
A lunar land rush is the most likely thing in the world (or, rather, out of it). As private companies gaze spaceward with dollar signs in their eyes, it's time to start settling some questions about space ownership, use and management.
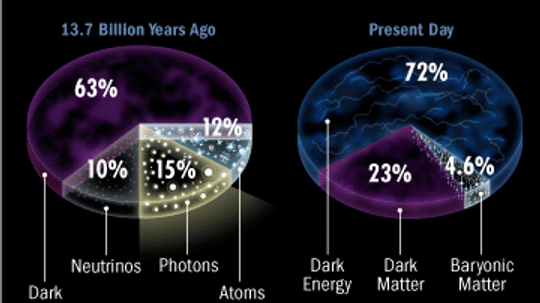
It wasn't so long ago that astronomers thought the universe contained normal matter, or baryonic matter, the base unit of which is the atom. But when it comes to the cosmos, there's always more than meets the eye. What else is hanging out in space?
Advertisement
What if your job were to protect life in the galaxy at all costs? That's exactly what the folks manning NASA's Planetary Protection office do, and bunny suits are just the beginning.
One tragic, moonless night in April 1912, the Titanic slid into the depths of the North Atlantic Ocean -- for good. A crew of Texas State academics suggested that Earth's favorite satellite may have some explaining to do.
How galaxies get their shapes and evolve is widely debated.
By Mark Mancini & Yara Simón
It's the first interstellar rock we've ever found!
Advertisement
It wasn't quite as loud as you might imagine.
The term "blue moon" dates back to at least the 16th century. Since then, it's had several different definitions, many of which are contradictory. So what's a blue moon today?
By Mark Mancini
And if we're going to get technical about it, neither do those of us here on Earth.
Energized subatomic particles bombarding Earth from outer space can cause the electronics inside laptops, cell phones and other devices to crash.
Advertisement
Yep, 'Oumuamua was probably kicked out of its own star system by an overbearing gas giant like Jupiter.