Cellular & Microscopic Biology
Cellular and microscopic biology allow scientists to study cells and microorganisms. Cellular biology is the study of cells, including their structure and function. Microbiology is the study of microorganisms, which include algae, bacteria, and viruses.
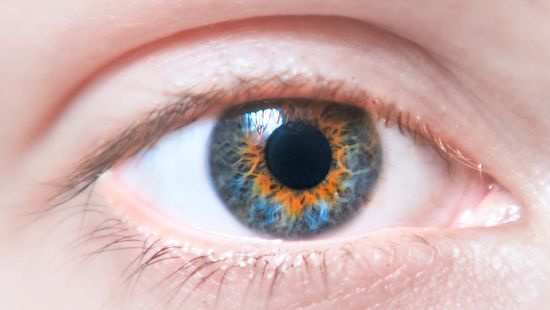
Central Heterochromia: When to Worry About Eye Color

10 Types of Noses to Spot in a Crowd

3 Major Types of Mushrooms: Edible, Wild and Poisonous

3 Types of Trees You'll Find All Over the Planet

A Corpse Flower Can Grow Over 12 Feet (3.7 Meters) Tall

Indica vs. Sativa: How to Distinguish Between Cannabis Plants

Neanderthal vs. Homo Sapien: Separate Species With Different Fates

Howstuffworks Interviews: Extinction Level Events with Annalee Newitz

What will the Earth look like in 50,000 years?

Is a Woolly Mammoth Clone Even Possible?

The Most Common Hair Color Isn't Blonde

What Is the Most Common Eye Color? Over 70% of People Have It

9 Types of Intelligence: The Many Ways to Expand Your Mind
Phineas Gage and the Birth of Modern Neuroscience

Call of the Void: A Counterintuitive Form of Self-preservation
Learn More
In scientific research, knowing the difference between in vivo vs. in vitro methods is essential for interpreting results and designing new experiments. These two approaches help researchers understand complex biological phenomena and advance medical knowledge in very different ways.
In science, people commonly use the terms "hypertonic" and "hypotonic" when describing the concentration of solute particles in solutions. But what exactly is the difference when it comes to hypertonic vs. hypotonic solutions?
By Marie Look
Your phone might look clean, but in reality, it's harboring germs, viruses and bacteria. So stop doomscrolling in the bathroom.
Advertisement
It's kind of amazing that no two fingerprints are alike, not even for identical twins! But why is that?
By Alia Hoyt
The Ophiocordyceps unilateralis fungus makes a mockery of ant free will. But how does it take over the ant body to control its host?
New studies suggests your gait may be able to predict something deeper than just a temporary mood.
Worried that we're running out of effective antibiotics? Never fear. Scientists are plundering cockroach brains and other surprising sources to create new lifesaving medications.
Advertisement
Lots of Americans believe that getting the flu is no worse than getting a cold. Or that the flu vaccine can give them flu. We separate truth from fiction.
When you get sick, your illness can be caused by several different factors. Learn why you get sick at HowStuffWorks.
The results of three recent studies show that an uncircumcised man is twice as likely to contract AIDS from an infected woman as is a circumcised one.
By Julia Layton
HIV continues to be a major global public health issue, having claimed more than 35 million lives so far.
By Kevin Bonsor & Oisin Curran
Advertisement
Learn about weight gain and the processes going on in your cells.
Influenza, Ebola and COVID-19 are all viruses. Find out what a virus does to your body and how to decrease your chance of exposure.
Researchers are working on ways to engineer viruses to attack cancer cells, killing the disease without radiation, medicine or surgery. How do the viruses know what to kill?
By Josh Clark
The journal "Nature" recently published a paper describing how a cell transplant had allowed blind mice to see again. What does this mean for humans?
Advertisement
You've heard it on the lips of every newscaster and seen it in the pages of every newspaper and Web site: swine flu. Just how worried should we be about the 2009 version of the H1N1 virus?
Are you the first to complain when it's too hot or too cold at work? Extremophiles have news for you: Suck it up. These hardy microbes make most of us humans seem like whimpering Goldilocks, and studying them may tell us more than you might imagine.
The human body is composed of about 10 trillion cells. Everything from reproduction to infections to repairing a broken bone happens down at the cellular level. Find out all about cells.
Your body temperature has an important role to play in fighting off infections from viruses like the flu. Here's how it works.
Advertisement
How can spam e-mail help fight HIV? Find out how spam e-mail and HIV are linked and learn about new methods for HIV treatment.
By Josh Clark
If you've kept up with the news lately, you've probably heard dire warnings about avian flu, or bird flu. In this article, we'll review the basics of how viruses and influenza work, and we'll learn the answers to these and other questions about avian flu, including whether it is likely to cause a global flu epidemic.
Hand sanitizers can only get you so far in preventing a viral infection. Scientists are discovering how visible light can be used to destroy viruses. Learn about the laser technique and what it means for the future.
You may be familiar with the medieval "Black Plague," but did you know that bouts of plague still break out today? Find out what causes an outbreak, why plague still exists and how the plague has influenced history.
By Tracy V. Wilson & Alia Hoyt
Advertisement
While most flu sufferers moan and groan for about a week and then return to work, the flu season creates more than just discomfort and a costly loss of work days.
We hear about them on the news and we listen to politicians argue for and against them using them to treat disease. Learn all about stem cells and the research, challenges and controversy that surround them.