Biological Fields
Biological fields are the different areas of study related to biology, such as botany, genetics and conservation. The various biological fields differ greatly in size, scope and methodology but all relate to the study of life.

3 Types of Trees You'll Find All Over the Planet

A Corpse Flower Can Grow Over 12 Feet (3.7 Meters) Tall

Indica vs. Sativa: How to Distinguish Between Cannabis Plants

In Vivo vs. In Vitro Trials (and Why Combining Both Is Best)

Hypertonic vs. Hypotonic Solutions: Differences and Uses

Your Phone Is a Germ Factory, So Stop Taking It to the Toilet

Neanderthal vs. Homo Sapien: Separate Species With Different Fates

Howstuffworks Interviews: Extinction Level Events with Annalee Newitz

What will the Earth look like in 50,000 years?

Is a Woolly Mammoth Clone Even Possible?

The Most Common Hair Color Isn't Blonde

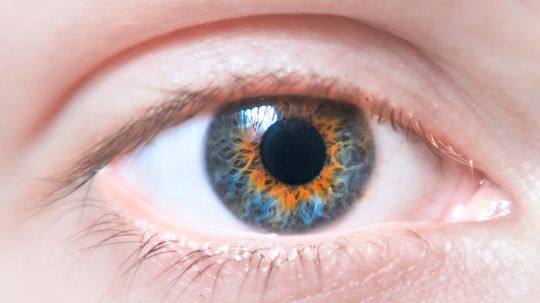
What Is the Most Common Eye Color? Over 70% of People Have It

9 Types of Intelligence: The Many Ways to Expand Your Mind
Phineas Gage and the Birth of Modern Neuroscience

Call of the Void: A Counterintuitive Form of Self-preservation
Learn More
Ever looked closely into someone’s eyes and noticed a vibrant ring of color encircling the pupil, distinct from the rest of the iris? That eye-catching trait is called central heterochromia, and it's more common than you might think.
Take a glance around any crowd and you’ll notice one thing: Noses come in all kinds of shapes and sizes. From sleek and straight to curved and prominent, the many types of noses play a big role in defining our unique facial features.
Some types of mushrooms are delicious and nutritious, while others are deadly and should never be eaten. Learning how to tell them apart is essential for both food lovers and foragers; knowing the difference between edible mushrooms and poisonous mushrooms can literally be a matter of life and death.
Advertisement
The natural world is a finely-tuned balance of biotic (living) and abiotic (nonliving) components that shape our environments. Various biotic factors directly affect processes like population growth, plant growth and nutrient cycling.
By Ada Tseng
Have you ever wondered what the largest living organism on Earth is? Well, you might be surprised to learn that it's not a giant blue whale or a sequoia tree; it's a fungus!
By Mack Hayden
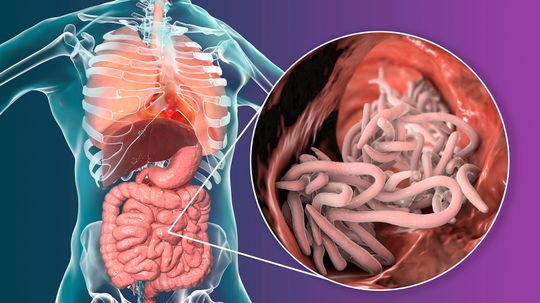
We're about to dive into the world of parasitology, taking a close look at one of the most common parasitic worms infecting humans: Ascaris lumbricoides. This large roundworm is responsible for a type of intestinal nematode infection that affects millions of people worldwide, especially in areas with poor sanitation.
By Mack Hayden
Jack Black does it. Wyclef Jean does it. And chances are, you do it, too. Everyone's a rock star in the bathroom. And there's a scientific explanation behind our soapy musical stylings.
By Debra Ronca
Advertisement
From tobacco smoke enemas to whirling chairs, doctors have tried almost everything to cure human disease.
A funny thing happens when you live in complete darkness. You lose your eyesight. At least that's what's happened to the species that have evolved inside our deepest, darkest caves.
By Debra Ronca
They might look like piles of goop, but slime molds can think and seemingly make decisions without a brain.
What are the chances there are still large, undiscovered animals on the planet? More likely than you might think.
By Diana Brown
Advertisement
On the surface, Antarctica may seem like a barren landscape. But underneath, in massive ice caves, life may be abundant.
By Amanda Onion
There are many myths and stigmas associated with leprosy, almost all completely incorrect. It's not a very contagious disease, and it's easily treatable. What else is wrong in the common beliefs about Hansen's disease?
Commensalism is a form of cooperation among species in which one species benefits from another without the first one suffering any harm from the relationship.
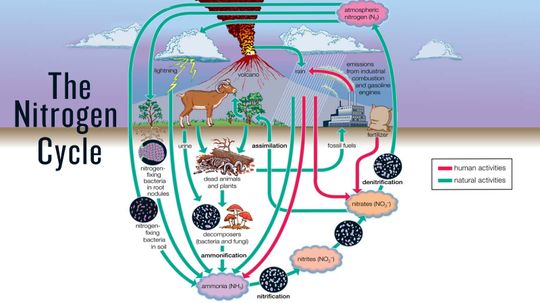
The nitrogen cycle is the system by which nitrogen is converted into different chemical forms, some usable to humans and animals and some not, as it circulates among the atmosphere, the land and the oceans.
Advertisement
Amanita phalloides is non-native to the North American continent, introduced to California from Europe, and rapidly spreading.
Bezoars are concretions found in the stomachs of animals that were once believed to cure poisoning and plague.
By Loraine Fick
For years, speculation has surrounded the government's high security animal disease research center, which is slated to close in 2023.
Horseshoe crabs have blue blood that can detect toxins, a rare ability that's threatening their survival.
By Loraine Fick
Advertisement
A strange, but surprisingly accurate, ancient Egyptian pregnancy test survived for millennia and was spread around Africa and Europe because it was just that effective.
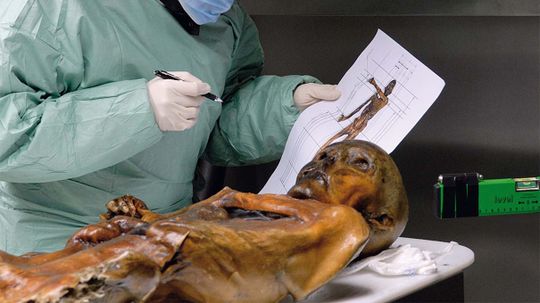
Researchers say that Otzi, the ancient man found in the Alps in 1991, lived on a diet loaded with fat to maintain warmth and energy in his cold, high-altitude environment.
How do we consider a Thing with no edge? Ecosystem ecologists are always trying.
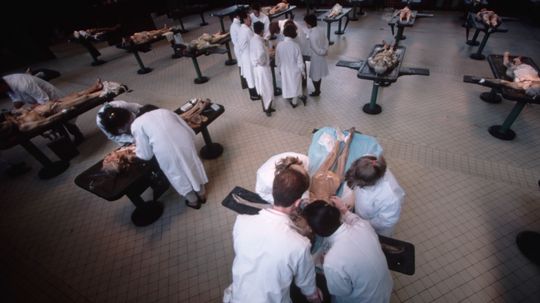
There's a great need for people to donate their bodies to science but not many people think about doing it. What happens to your body after you make that decision?
Advertisement
Distilleries call this evaporative substance "angel's share" and promise that it's not dangerous, but nearby residents find it coating everything around them and aren't so sure.
Heat waves are becoming supercharged as the climate changes. How hot is too hot for normal daily activity, even for young, healthy adults?
By W. Larry Kenney, Daniel Vecellio, Rachel Cottle & S. Tony Wolf